Spotting blood in urine can be an unpleasant experience. More so is not knowing what could be the reason for blood in urine. We know that some Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs for short) can cause this symptom. Here, we will talk about STDs that cause blood in urine.
The two most likely STDs that can cause blood in urine for females and males are Chlamydia and Gonorrhea.
In this guide, we cover various aspects of what could be the reason for blood in urine for both males and females. We discuss Chlamydia and Gonorrhea in detail and also recommend one of the most trusted STD diagnostic provider in our network.
Below is the table of contents for this article:
- Why do I see blood in urine?
- What are the types of STDs that cause blood in urine?
- How can I get tested sitting at home for STDs causing blood in urine?
- How much is the cost of STD Testing near me in the US?
- Another Reason for Blood in Urine for Males
- List of Other Causes of Blood in Urine
- Why do I feel a burning sensation while urinating?
- What is the treatment for blood in urine?
- What is hematuria?
- What is STD?
- What are the signs and symptoms of an STD?
Why do I see blood in urine?
Finding blood in the urine can be stressful and one starts to immediately wonder what could be the reason for this. The good news is that there is no reason to panic as blood in urine is mostly due to diseases that can be managed relatively easily and cured with the right diagnosis and medication.
Before we get into more problematic reasons for blood in urine, we cover the simplest explanation first. Sometimes the urine may be red or dark brown due to consumption of beetroot or some food color dye. This condition is completely harmless and the color of urine will go back to normal as the digestive system clears the culprit food out of the system.
The STDs that most commonly cause blood in the urine are Chlamydia and Gonorrhea. We tell you more about these diseases and how to get tested for them in the below sections.
What are the STDs that cause blood in urine?
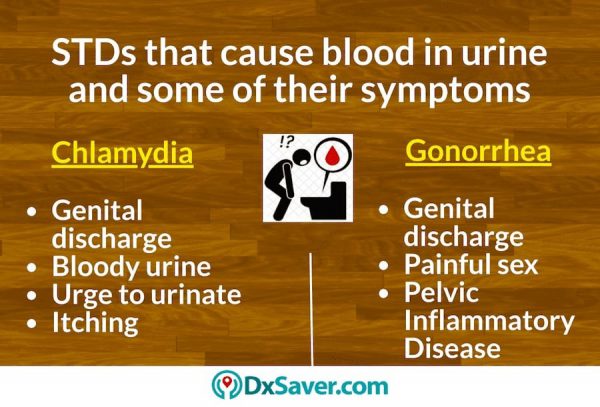
Chlamydia and Gonorrhea are the two types of STDs with blood in urine symptoms.
1. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the highest reported sexually transmitted infections in the U.S. One of the symptoms of Chlamydia is blood in urine. The microbes sometimes create an infection in the urethra which can cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). Chlamydia can cause pain and discomfort during urination such as a burning sensation while urinating and a urge to urinate frequently.
In women, untreated chlamydia infection could travel from the cervix to the fallopian tubes, which can then cause more noticeable symptoms of chlamydia including heavy periods, itching, swelling in the vulva, dysuria, and vaginal discharge.
If the symptoms are ignored, then the infectious bacteria can cause serious damage to the kidneys and urinary tract. Ultimately, leading to permanent kidney problems that can take a long time for treatment.
2. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is the other STD that has blood in urine as one of the symptoms. In men, gonorrhea or the clap STD shows other symptoms like abnormal discharge, testicular and scrotal pain, inflammation around the penis. In rare cases, it may also result in infertility.

- Pain or bleeding during sex
- Bleeding between periods
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
To get tested for Gonorrhea and Chlamydia, we cover an excellent diagnostic lab chain option below.
How much is the cost of STD Testing near me in the US?
STD testing cost ranges between $24 and $444 in different labs and facilities across the U.S. No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours or shop the STD home testing kit. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days.
Our preferred STD testing partner is STDCheck. They have an vast network of labs across the country. You are sure to find a lab near your home or office. Just click on the photo or the link given below and you will be taken to their website. You can then book either two tests separately or a package of tests to get tested for multiple STDs simultaneously at a discounted cost.
Another Reason for Blood in Urine for Males
Prostate gland enlargement affects nearly 50 percent of males between the age group of 51-60 years, and up to 90 percent of old men above the age of 80.
The prostate is a gland that sits below the bladder and in front of the rectum in the male reproductive system, it aids in semen production. As men get older, the prostate gland tends to enlarge and press down on the urethra, making urination difficult. The bladder may compensate by pushing harder to eliminate urine, which could result in damage and bleeding.
The medical expression for an enlarged prostate is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). Blood in urine is one of the key symptoms of BPH.
BPH symptoms are:
- Urgent need to urinate
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting urination
- Need for strain while passing urine
- Intermittent urine flow
- A sense of full bladder even after urinating
- Blood in urine
What are the Other Causes for Blood in Urine?
Following are some of the causes other than STDS for blood in the urine. However, if you are sexually active and having more than one sex partner, then STDs will likely be the cause.
1) Infection (urinary tract infection/sexually transmitted infection)
A. Chlamydia STD – Chlamydia is caused by microbes and sometimes it can result in serious infection in the urethra which can lead to urinary tract infection (UTI). Thus chlamydia can lead to blood in the urine.
B. Gonorrhea STD – Gonorrhea is one of the most commonly reported sexually transmitted infections in the U.S. The bacteria affects the moist area like the genitals, urethra, rectum, vagina, and throat. Bloody urine, itching, abnormal discharge are the symptoms of this STI. Gonorrhea is an STD with blood in urine as one of its symptoms.
C. Urinary Tract Infections – They are of two types i.e. lower tract infection (also known as bladder infections) and upper tract infection. UTIs can be easily treated but if it is left untreated it can lead to severe kidney problems resulting in permanent kidney damage.
2) Nephrolithiasis
Nephrolithiasis refers to kidney stones that are slowly formed inside the kidney due to deposits of minerals and acid salts, they often cause irritation and discomfort while passing urine. Kidney stones are also one of the main reasons to spot blood in the urine.
3) Kidney disease
Kidney diseases like chronic kidney disease (CKD) also known as kidney failure can also be the cause of blood in the urine. This can be a result of excessive fluid waste that gets deposited in the kidney where it can no longer filter.
4) Prostate gland enlargement
Prostate gland enlargement causes blood in urine in men and it is not prostate cancer. As men get older, the prostate gland gets enlarged. This can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder.
5) Cancer
Pancreatic cancer and liver infections cause dark brown-colored urine. Skin cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, or kidney cancer can also result in colored urine.
6) Injury
Kidney injury due to an accident or through sports.
7) Drugs
The cause for blood in the urine (hematuria) can be a result of taking certain drugs like such as aspirin, cyclophosphamide, heparin, and penicillin.
8) Strenuous exercise
“Exercise-induced hematuria” means strenuous exercise includes very intense exercises, long endurance events, and poor hydration. In general, the urine clears 72 hours after exercise. Sometimes, if the blood in urine keeps appearing after 72 hours, it needs to be reported.
9) Hematologic disorders
Conditions like sickle cell anemia, hereditary illnesses, or cystic kidney disease. Also, tumors in the bladder, kidney, or prostate might be a reason for blood in the urine.
In short, if you detect bright red blood in your urine or if your urine has turned red or brown because it has blood in it then we recommend consulting a medical physician if this symptom persists for several days.
Why do I feel a burning sensation while urinating?
Pain or burning sensation during urination can be a sign of Sexually Transmitted Infections. STDs that can cause a burning sensation while urinating are:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea (the clap STD)
- Trichomoniasis
- Herpes
Although, it can occur due to kidney stones or urinary tract infections. You should also check the color of your urine to detect the presence of blood.
Abnormal discharge from genitals
Unusual discharge from the penis/vagina is generally a symptom of an STD or another infection. STDs that can cause discharge include:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Trichomoniasis
These infections can be cured with antibiotics. It’s important to take the medication and complete the full course of it as it has prescribed.
What is the treatment for blood in urine?
Firstly, diagnosis of the cause of blood in urine is vital and the treatment has to be prescribed accordingly.
If the blood in urine is caused due to STDs like chlamydia and gonorrhea, it can be treated using antibiotics and antiviral drugs like Azithromycin and Ceftriaxone. It is very important to take antibiotics as prescribed by the physician even if the symptoms abate.
What is hematuria?
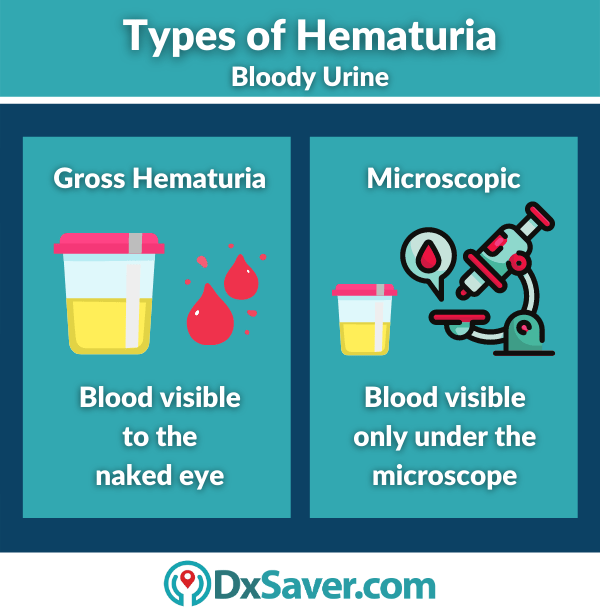
The medical name for blood in urine is “hematuria”. There are two forms of hematuria, one, if the blood is visible to the naked eye, it’s macroscopic hematuria, or “visible hematuria”. Or, if you need lab tests to confirm the appearance of red blood cells, then it’s “non-visible hematuria” or microscopic. Generally, seeing blood at a noticeable amount or colored urine ( pale yellow color, pink, red, brownish-red, or tea-colored), is what physicians call gross hematuria.
The kidney eliminates the urine. The blood in the urine must have occurred from within the kidneys, or urinary bladder.
What is an STD?
Sexually Transmitted Disease is the full form of STD and also known as STIs. Sexually transmitted diseases are infections caused by germs like bacteria, yeast, viruses, and parasites that grow in the genital areas as they are moist and warm and can be spread through sexual contact with the infected person. STIs are generally transmitted through sexual contact including anal, vaginal, or oral sexual contact, with the infected person and sometimes through blood or skin contact.
There are more than 20 types of common sexually transmitted diseases, they include Hepatitis Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Herpes, HIV, Trichomoniasis, and HPV.
What are the signs and symptoms of an STD?
The signs and symptoms of STD don’t show up during the early stages and the infected person can be walking around with STD for several without evening knowing about it. Usually, the signs appear in the second week since the contraction of the disease. The most common symptoms of STDs are
- Abnormal vaginal/penile discharge
- Pain while urinating
- Pain in the back or lower abdomen
- Heavy menstrual bleeding in women
- Blood in urine
- Swelling and pain in the testicles
- Anal itching
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Headache
- Joint pain