
According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), an estimated number of 13,800 new cases of cervical cancer will be diagnosed and 4,290 women diagnosed with cervical cancer will die in the year 2019 in the U.S. Cervical cancer is more commonly found in the women who fall under the age group of 35 and 44 years. This cancer can be cured only when it is diagnosed at the early stages. Most of the women affected with cervical cancer do not show any symptoms at an earlier stage. So we highly recommend every woman above 30 years of age to get tested for cervical cancer screening test at least once every year.
The article below covers all the significant topics related to cervical cancer like cervical cancer screening test cost, causes of cervical cancer, types, early symptoms, stages of cervical cancer, cervical cancer treatment and prevention, and how to get tested for the cervical cancer screening test.
- Cervical cancer screening test cost.
- What is cervical cancer?
- What are the causes of cervical cancer?
- Types of cervical cancer.
- What are the signs and symptoms of cervical cancer?
- How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
- Stages of cervical cancer
- How to treat cervical cancer?
- Are there any side-effects in cervical cancer treatment?
- Can cervical cancer be cured?
- How to prevent cervical cancer?
- Provider Locations
For our readers, who are very much interested in knowing the cervical cancer screening test cost beforehand, we would like to begin with that section.
How much does the cervical cancer screening test cost?
Our cervical cancer testing provider offers the cervical cancer screening home test kit at $79. No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days. Doctor consultation is also available for further treatment or any kind of medical advice.
The following table shows the cervical cancer screening test cost at one of our partner laboratory (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
myLab Box(Home Test Kit)
| Offer Price$79 |
Cervical cancer testing
Testing for cervical cancer is a two-step process.
1. Cervical cancer screening test: Generally, PAP smear and HPV (human papillomavirus) tests are the cervical cancer screening tests done to detect the abnormal changes in the cervical cells. However, HPV testing is the most accurate test to diagnose women who are at risk of developing cervical cancer. The HPV screening test looks for the high-risk HPV types that might cause cervical cancer. This test result has a positive or negative outcome.
2. Cervical cancer advanced testing: When the screening test results are positive, some advanced diagnostic tests like a biopsy, colposcopy, and pelvic ultrasound will be ordered by your physician to know the exact stage of cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer screening test cost with insurance
Most of the health insurance policies in the U.S. cover the cost of both cervical cancer screening tests and advanced diagnostic tests to encourage women to get tested for cervical cancer. But the coverage offered by private health insurance policies and national health insurance programs like Medicare and Medicaid varies widely. So we recommend you to check the coverage of your health insurance plan before getting tested.
Our cervical cancer testing provider offers the screening test, HPV test at the lowest cost and does not accept any health insurance. But, on request, they can provide you with an itemized receipt containing all the details like the name and code of the test, and CPT code that is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cervical cells i.e. when the abnormal cells grow in the cervix, multiply rapidly, and form a tumor. Cervix is the narrow part of the woman’s uterus that connects the lower part of the uterus to her vagina. It is often referred to as the neck of the womb.
Cervical cancer used to be one of the leading causes of cancer deaths in women in the U.S. This changed when cervical screening tests became widely available. Cervical cancer can be cured if it is diagnosed and treated at the early stages. So we recommend everyone above the age of 30 years to get tested for the cervical cancer screening test.
What are the causes of cervical cancer?
In most cases, cervical cancer is caused due to the longstanding infection of human papillomavirus (HPV). This infection is very common among sexually active women as this virus is transmitted through sexual contact and skin to skin contact with the infected person. There are more than 100 types of HPVs and not all types cause cervical cancer. Certain types of HPVs that are linked to cervical cancer are called high-risk HPVs. The high-risk HPVs can also cause mouth cancer, throat cancer, and anal cancer in both men and women.
Doctors also say that the following factors can increase the risk of developing cervical cancer in women.
- Multiple sex partners as it increases the chance of acquiring HPV
- Early sexual activity
- Smoking
- Having other sexually transmitted diseases
- A weakened immune system
- Long term use of contraceptive birth control pills
Types of cervical cancer
The type of cervical cancer is classified based on the type of cell from where cancer started. The type helps the physician to determine the prognosis and treatment. The following are the types of cervical cancer.
1. Squamous cell carcinoma
This is the most common type of cervical cancer. It develops in the thin, flat cells (squamous cells) lining the outer part of the cervix that projects into the vagina.
2. Adenocarcinoma
This type of cancer develops in the column-shaped glandular cells lining the cervical canal.
Very rarely, cancer develops in other cells of the cervix.
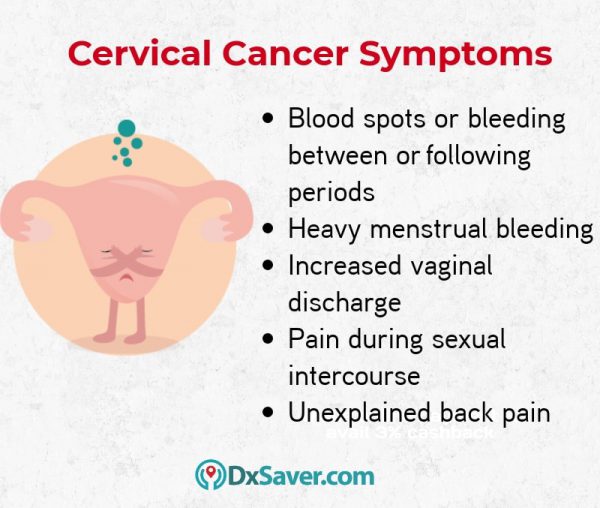
What are the signs and symptoms of cervical cancer?
Most women with cervical cancer do not show any symptoms until their advanced stages. The most common symptoms of cervical cancer in its advanced stages are
- Pain in the pelvis
- Back pain
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after sexual intercourse or after menopause)
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain during intercourse
- Kidney failure
- Painful urination
- Urge to urinate more frequently
These symptoms do not mean that you have cervical cancer. Other diseases can also cause similar symptoms. But we highly recommend consulting a physician when you experience the above-mentioned symptoms for a significant period of time.
How is cervical cancer diagnosed?
Generally, the screening tests are done initially to diagnose the abnormal changes in the cervical cells that might lead to cancer. When the screening test results indicate the abnormality, some advanced diagnostic tests are done to know the exact stage of cancer.
Screening tests:
1. Pap smear test
During this test, your physician will use a small brush or a swab to take some of your cervical cells. Then, the sample cells taken are sent to the lab for diagnosing the abnormalities.
2. HPV genotyping
This test involves testing the cells of the cervix for any type of high-risk HPV infection that might lead to cervical cancer.
Advanced diagnostic tests:
1. Cone biopsy
Cone biopsy is also known as conization and it is mostly performed in the hospital under anesthesia. During this procedure, a small cone-shaped portion of the cervix is removed for examination.
2. LEEP
LEEP refers to the “Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure”. During this procedure, a thin electrified wire is used to take a small tissue sample from the cervix.
In addition to the above-mentioned tests, your physician might also recommend other imaging tests like MRI, CAT scan, pelvic ultrasound, and colposcopy (colposcopy is a procedure done using a colposcope to closely examine the cervix, vulva, and the vagina) for accurate diagnosis and correct treatment.
Stages of cervical cancer
Staging helps the physician to decide the most effective treatment for cervical cancer. There are 4 stages (stage I to stage IV) of cervical cancer. The four stages are explained below.
Stage 1 – Cancerous cells are present in the cervix and have grown into the deeper tissues of the cervix, possibly to the uterus and the nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 2 – At this stage, cancer has moved beyond the cervix and uterus but not as far as the pelvic walls and the vulva (lower part of the vagina).
Stage 3 – Cancerous cells are grown in the pelvic walls and the lower part of the vagina, possibly blocking the ureters. Ureters are the tubes that carry urine from the bladder.
Stage 4 – At this stage, the cancerous cells grow in the bladder and rectum and also spread to distant organs such as the liver, lungs, bones, and lymph nodes.
How to treat cervical cancer?
If you have been diagnosed with cervical cancer, your physician will decide the treatment depending on the stage of cervical cancer. In most cases, people diagnosed with cervical cancer have several treatments at the same time. The following are the key treatments for cervical cancer.
1. Surgery
Surgery is the most common method for treating cervical cancer at its initial stage when cancerous cells are only present in the cervix and have not spread to other parts. During the surgery, the cervix will be removed which is called trachelectomy. In some cases, when cancer is spread to the uterus, the uterus will also be removed which is known as hysterectomy. Surgery can cure cervical cancer and prevent the recurrence of cancer.
2. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high energy beams (like X-rays or protons) to kill the cancerous cells. It is mostly preferred for the advanced stages of cervical cancer. It can also be used after surgery to prevent the recurrence of cancer. Radiation therapy can be given either externally or internally.
1) External beam radiation therapy – A machine outside the body directs the energy beams at the cancerous cells to destroy them.
2) Internal (Brachytherapy) – Physicians will place a device with radioactive material inside the vagina for fewer minutes to kill the cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses chemicals or drugs to kill cervical cancer cells. The drugs may be injected into the vein or given orally. Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to control the symptoms of cervical cancer in its advanced stage.
4. Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is mostly combined with chemotherapy to treat the advanced stage of cervical cancer. This therapy uses drugs focusing on specific weaknesses present within the cancerous cells. The drugs block the weaknesses and kill the cancer cells.
5. Immunotherapy
This treatment is preferred only when cervical cancer reached the advanced stage and other treatments are not working. Immunotherapy uses specific drugs that help the immune system fight against cancer. Generally, the immune system does not fight against cancer as the cancer cells produce a specific protein making them undetectable by the immune system. The drugs used in immunotherapy helps the immune system to identify cancerous cells and fight against them.
Are there any side-effects of cervical cancer treatment?
Treatment for cervical cancer can lead to a variety of side effects. Consult your physician immediately when you start noticing them. Though they cannot be completely cured, they can be controlled with some medications. The following are some of the side effects caused due to cervical cancer treatment.
- Fatigue
- Bowel dysfunction
- Loose stools
- Anemia
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss or weight gain
- Loss of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Bladder problems
- Menopause
- Sexual dysfunction
- Fertility problems
- Osteoporosis (weakened bones)
- Rarely, heart diseases

Can cervical cancer be cured?
Cervical cancer is curable only when it is diagnosed and treated at an early stage. When cancer has spread to other parts (metastatic cervical cancer) beyond the cervix, it cannot be cured but, it is possible to slow down the progression, prolong the lifespan, and relieve the symptoms.
How to prevent cervical cancer?
The following are some of the ways that can prevent you from getting cervical cancer or lower the risk of getting cervical cancer. They are
- Regular screening tests – Screening tests can detect the abnormalities in the cervical cells at an early stage.
- Practice safe sex – Safe and protected sex lowers the risk of acquiring HPV infection.
- Quit smoking – Studies have shown that smoking cigarettes increases the risk of getting cervical cancer.
- Get vaccinated – Two vaccines such as Cervarix and Gardasil are available to protect against the high-risk HPV infections that are more likely to cause cervical cancer.
Provider Locations
The cervical cancer screening test can be done in any of the following locations across the U.S. by shopping the home test kit. To know the cervical cancer screening home test kit cost, refer to the first section of the article.
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order anytime before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- Gonorrhea Symptoms in Men
- At-Home Chlamydia Testing Cost in the U.S.
- Eye Chlamydia Symptoms
- Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Test Cost in the U.S.
- Cost of Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) Test in the U.S.
- How much does the Homocysteine Test Cost in the U.S?
- Lyme Disease Test Cost in the U.S.
- Celiac Disease Test Cost in the U.S.
- Cost of Ferritin Test Cost
- Types of STD that causes dry skin
- CA 125, Ovarian Test Cost in the U.S.
- HIV Testing Providers in the U.S.
- Do STDs Spread Via Kissing?
- What STDs cause Sore Throat?
- What is Oral Chlamydia? Get Tested for Chlamydia STD at-home
- Lipid Profile Testing, Normal Levels & Diagnosis
- Causes of Penile Rashes and Other STD Symptoms in Men
- Oral STDs: Names, Symptoms, Treatment and Testing Cost
- Parkinson’s Disease – Know more about its Symptoms, Stages, Diagnosis & Treatment
- LDH Hormone Normal Levels, Abnormal Levels Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment





