Cells are the units that make up the human body. They grow and divide to make new cells. Usually, cells die when they are too old and damaged. Then, the new cell takes its place. Usually, cancer begins when genetic changes interfere with this orderly process. During such crisis cells start to grow uncontrollably. These old cells may then form a mass called a tumor. A tumor may be cancerous. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread from one organ to another organs.
In the United States, colon cancer is the third most common cause of cancer-related to death. Colorectal cancer or colon cancer is cancer that starts in the rectum or in the colon. Both of these organs are in the lower portion of the digestive system. The colon is nothing but the large intestine and the rectum is at the end of the colon. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS) around 1 in 22 men and 1 in 24 women will develop colon cancer during their lifetime. So we highly recommend every individual to get tested for colon cancer at least once in a year.
The article below covers all the relevant topics of colon cancer including the symptoms of colon cancer, causes of colon cancer, its treatments, colon cancer stages, how to get tested, and its preventions.
- Types of colon cancer
- Symptoms of colon cancer
- Colon cancer stages
- Colon cancer causes
- What are the treatments for colon cancer?
- Complications of colon cancer
- Prevention
- How to get tested?
- Providers locations
Types of colon cancer
Colon cancer sounds clear-cut, but there’s more than one type of colon cancer which depends upon where the cancerous cells are formed. The most common type of colon cancer begins from Adenocarcinomas. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), Adenocarcinomas cause 96 percent of all colon cancer cases. Unless your Physician specifies, your colon cancer is likely this type. Usually, the Adenocarcinomas from within mucus cells in the colon or in the rectum.
But less commonly, colon cancers are caused by other types of tumors as well, that is:
- Lymphomas: It can form either in lymph nodes or in the colon first
- Carcinoids: This starts in the hormone-making cells within the intestines
- Sarcomas: It forms in the soft tissues like muscles in the colon
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: It generally starts off as benign and then becomes cancerous. They usually form in the digestive tract, but rarely in the colon
Symptoms of colon cancer
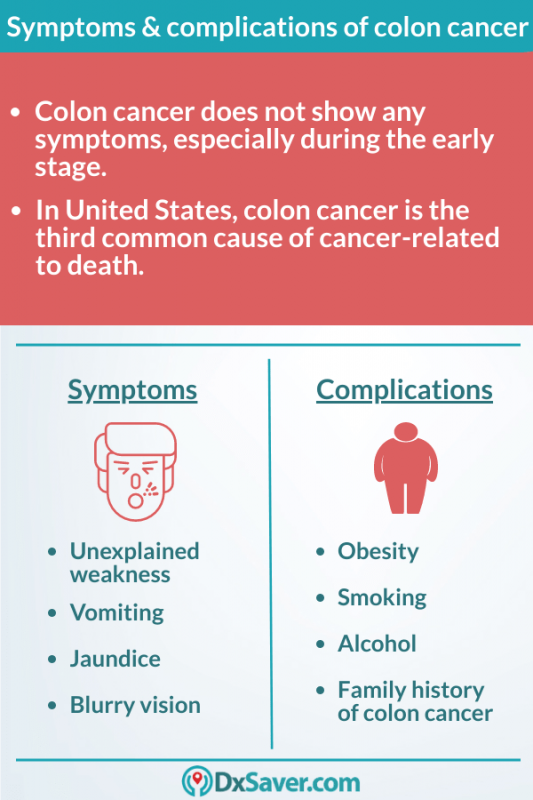
Colon cancer does not show any symptoms, especially during the early stages. Even when the symptoms appear, they vary depending upon the cancer size and the place where it has appeared in the large intestine. Early stages symptoms include:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Change in stool shape
- Blood in the stool
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Excessive gas
- Abdominal cramps
- Abdominal pain
If you notice any of these symptoms, make an appointment with your physician immediately.
Colon cancer stage 3 or 4 symptoms or late-stage symptoms
Colon cancer symptoms are mostly noticeable only in the late stages. In addition to the above symptoms, you might also experience the following:
- excessive fatigue
- unexplained weakness
- unintentional weight loss
- change in the stool that lasts longer than a month
- vomiting
If colon cancer spreads to other parts of your body, you may also experience the following symptoms:
- jaundice
- swelling in hands and feet
- breathing difficulties
- chronic headaches
- blurry vision
- bone fractures
Colon cancer stages
There are different ways of assigning a stage of colon cancer. Your physician will determine the stage by how far cancer has spread or the size of tumors.
Colon cancer stages are as follows:
- Stage 0: It is also known as “carcinoma in situ”. During this point, the cancer is at a very early stage. It has not grown farther than the inner layer of the colon and it is usually very easy to treat.
- Stage 1: At the stage, cancer has grown into the next layer of tissue but has not reached the lymph nodes or any other organs yet.
- Stage 2: Cancer has reached the outer layers of the colon at this point, but it has not spread beyond the colon such as other organs.
- Stage 3: At this point, cancer has grown through the outer layers of the colon, and it has reached one to three lymph nodes. But it has not spread to distant sites, however.
- Stage 4: It’s a very critical stage where cancer has reached other tissues beyond the wall of the colon. As stage 4 progresses, colon cancer reaches the other parts of your body.
Colon cancer causes
Doctors and researchers are still studying the causes of colon cancer. They aren’t certain what causes colon cancer. While there’s a growing list of risk factors, they act alone or act in combination to increase one’s risk of developing colon cancer.
(i)Precancerous growths
Abnormal cells which accumulate in the lining of the colon, forming polyps. These are basically small, benign growths in the colon. Removing these growths through surgery is the common preventive method to reduce the risk of colon cancer. If it’s left untreated, then the polyps can become cancerous.
(ii)Gene mutations
Sometimes colon cancer occurs in family members also. This is due to a gene mutation that passes from parent to child. These mutations don’t guarantee you’ll develop colon cancer, but they do increase your chances of passing on.
What are the treatments for colon cancer?
The treatment for colon cancer depends upon the state of your overall health and the stage of your colorectal cancer that will help your doctor create a treatment plan.
(i)Surgery
In the earliest stages of colon cancer, it might be possible for your physician to eradicate the cancerous polyps through the surgery itself. If the polyp isn’t attached to the wall of the bowels, then you’ll likely have an excellent outlook.
(ii)Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs that helps in killing cancer cells. In the case of colon cancer, chemotherapy is a helpful treatment which is performed after the surgery to destroy any remaining cancerous cells. Chemotherapy also helps in controlling the growth of the tumors.
(iii)Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses a powerful beam of energy, which is similar to that used in X-rays, to target and destroy cancerous cells before and after the surgery. Radiation therapy is commonly done along with chemotherapy.
(iv)Medication
In the United States, Food and Drug Administration approved that the drug regorafenib to treat the late-stage of colon cancer, it doesn’t respond to other types of treatment and has spread to other parts of the body. This drug works by blocking enzymes that promote the growth of cancer cells in the large intestine.
Complications of colon cancer
Some of the factors that may increase your risk of colon cancer include:
- Diabetes: People who have diabetes or insulin resistance have an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Obesity: People who are obese have a high risk of colon cancer and an increased risk of dying of colon cancer when compared with people having a normal weight.
- Smoking: People who smoke regularly may have an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Alcohol: Heavy consumption of alcohol increases your risk of colon cancer.
- Family history of colon cancer: You’re more likely to develop colon cancer if you have a blood relative who has this disease. Also, if more than one family member has colon cancer or even rectal cancer, your risk is even higher.
Prevention
Consider the following steps to reduce the risk of colon cancer by making changes in your everyday life:
- Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, which play a higher role in cancer prevention.
- Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all: If you choose to drink alcohol, limit the consumption of the alcohol you drink.
- Stop smoking: Talk to your physician about the ways to quit smoking that may work for you.
- Exercise most days of the week: Exercise at least 30 minutes on most days. If you’ve been inactive for a long time, then start slowly and build up gradually to 30 minutes.
- Maintain a healthy weight: If you are at a healthy weight, work to maintain your weight by adding a more healthy diet with daily exercise. Aim to lose weight by increasing the amount of exercise slowly and reducing the number of calories you intake.
How to get tested?
CEA blood test is done to measure the levels of CEA in the blood. Your physician will prescribe for a CEA blood test to detect the tumor cells. This CEA test is also used to diagnose Pancreatic cancer, Gastric, Ovary, and Lung cancer.
The following table shows the Colon cancer testing cost at one of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
Personal Testing Lab
| Offer Price$59 |
Providers locations
Colon cancer tests can be done in any of the following states at the provider’s location. To know the colon test cost at these locations, refer to the above table.
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order anytime before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- C-peptide test cost in the US
- Signs and Symptoms of Oral Syphilis
- CEA test cost in the US
- Diabetes test cost in the US
- Get Lowest Lipid panel test
- Herpes test cost in the US
- What are the symptoms of Lung cancer?
- GGT, Gamma-GT Blood Test Cost in the US
- How Much Does At-Home Drug Test Kit Cost in the US?
- ANA Test Cost in the US
- Anti-aging Testing Cost in the US
- C-Peptide Normal Levels, Test Results & Treatment
- Types of STDs that cannot be cured
- Is Itching a Symptom of STD?
- Herpes Vs. HPV: Differences, Symptoms, and Testing Cost
- Importance of CA 125 Testing & Ovarian Cancer in Women
- Oral STDs: Names, Symptoms, Treatment and Testing Cost
- What is throat cancer? Read more about its types, symptoms, and treatment
- Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer | More about Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment





