
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 30 million Americans have Diabetes and every 1 in 4 of those people, actually do not know they have Diabetes. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. So we highly recommend people with Diabetes to do routine Diabetes tests to monitor the blood sugar level. We also recommend people with normal blood sugar levels to get screened for Diabetes at least once in a year.
The article below covers all the relevant topics of Diabetes like the Diabetes test cost, types of Diabetes, symptoms, risk factors, complications, and how to get tested for Diabetes.
- Diabetes test cost
- What is diabetes?
- Types of diabetes?
- Symptoms of diabetes
- How is diabetes diagnosed?
- How is the Diabetes test performed?
- Is there any preparation required before the test?
- How is Diabetes treated?
- Normal blood sugar levels
- What are the risk factors and complications of Diabetes?
- How to prevent Diabetes?
- Provider Locations
For our readers who would like to know more about the different Diabetes tests and their cost beforehand, we begin with that section.
How much does the Diabetes test cost?
Diabetes test cost ranges between $61 and $69 in different labs and facilities across the U.S. The diabetes test cost also depends on the choice of your testing for specific Diabetes tests like Hemoglobin A1c test, Glucose test, Gestational diabetes test, etc., or testing for Diabetes (Diabetes profile test, Comprehensive Diabetes profile test, etc.) as a whole package.
No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days.
The following table shows the diabetes test cost at 2 of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) networks located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
HealthLabs
| Starting from$69 |
Personal Testing Lab
| Starting from$61 |
Diabetes test cost with insurance
Most of the health insurance policies in the U.S. cover the cost of Diabetes tests only once or twice a year. In case, if your physician recommends you to take the diabetes tests more frequently, then the cost should be paid out of your pocket. As the coverage offered by private health insurers and national health insurance programs varies widely, we recommend you to check with your insurance company.
Our diabetes testing providers do not accept any health insurance. But they can provide you an itemized receipt containing all the details like the test name and code, and CPT code which is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as Diabetes, is a metabolic condition where the body is not able to process the blood sugar (blood glucose), causing high blood sugar levels. Glucose plays a vital role in the body as it is an important source of energy for the cells to build up muscles and tissues. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the cells to absorb glucose or store glucose for future use. With Diabetes, either your body does not produce enough insulin or it cannot use the insulin effectively.
Diabetes explained in a short 5 minutes video:
Types of Diabetes
The different types of Diabetes are explained below.
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes was also known as “Juvenile Diabetes” as most of the people diagnosed with type 1 Diabetes were children and young people. But, then they found out that type 1 diabetes can occur in adults too. So, it is no longer called “Juvenile Diabetes”. Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the immune system destroys all the cells in the pancreas called beta cells. So the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin for the cells to absorb glucose which results in the high blood glucose levels causing this chronic condition. It is an auto-immune disease and this type of diabetes is very rare. Sometimes, pancreatic disease or injury wipes out the beta cells, resulting in the production of low insulin. This condition is called “Secondary Diabetes”.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes is the most common type of Diabetes. It is a long term disease that occurs because of the body’s resistance to insulin. So, the glucose stores in the blood which increases the blood sugar levels. There is no cure found for type 2 diabetes to date. A combination of proper diet, medications, and exercise can help you to reach and hold normal blood glucose levels.
3. Prediabetes
Prediabetes is like a pre-diagnosis of diabetes. This is a medical condition which shows that the blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes patients are at a higher risk of developing type 2 Diabetes. This condition tells you that you are on the way to Diabetes. A proper combination of a healthy diet and exercise can prevent you from getting type 2 diabetes.
4. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes is the condition of high blood sugar levels which occurs only in pregnant women. Some hormones produced by the placenta block the insulin which results in high blood glucose levels. This type of diabetes, if left untreated, can cause severe complications to the mother and the baby. To prevent yourself from getting gestational diabetes, follow a healthy diet that does not increase your blood sugar levels.
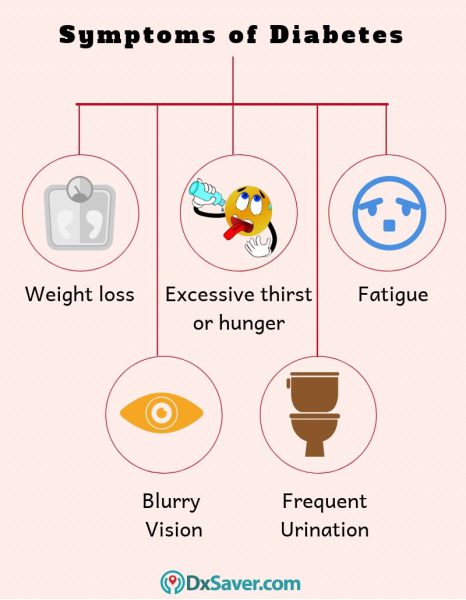
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms vary depending on the type of diabetes you have. The common symptoms of different types of diabetes are explained below.
- Increased hunger
- Increased thirst
- Unusual weight loss
- Blurry vision
- Tiredness
- Mood changes
- Frequent urination
- Sores or wounds that do not heal
In addition to the above, men with diabetes may experience decreased sexual drive, erectile dysfunction, and poor muscle strength. Women with diabetes may experience urinary tract infections and yeast infections. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes do not show any symptoms. It is usually diagnosed by an oral glucose tolerance test performed between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
How is Diabetes diagnosed?
Diabetes is diagnosed using simple blood tests. As the symptoms of Diabetes may not be evident and come on gradually, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) has recommended the people with the following conditions to be screened for diabetes at least once in a year.
- Body mass index (BMI) higher than 25
- Above 45 years of age
- Diagnosed with Gestational Diabetes
- Prediabetics
Your physician will order the Hemoglobin A1c test to check and monitor the blood glucose level in the body. This test shows the average blood sugar level in the last 3 months. If the A1c levels are higher than normal, your physician will order the following tests to diagnose diabetes.
- Random blood sugar test (blood sample taken at a random time)
- Fasting blood sugar test (blood sample taken after overnight fasting)
- Oral glucose tolerance test (sugary liquid is given orally after overnight fasting to test the sugar levels periodically)
To diagnose gestational diabetes, your physician will order the following screening tests.
- Initial glucose challenge test
- Follow-up glucose tolerance test
How is the Diabetes test performed?
All the above-mentioned tests are simple blood tests. The phlebotomist will wrap a tight elastic band around the upper arm to make the veins visible and swell with blood. Then, he will inject a needle into the vein to draw some blood. The collected blood sample is stored in a test tube and sent to the lab for analysis.
If you are diagnosed with Diabetes and your physician suggests you monitor the glucose level more frequently, you are not required to visit the lab more often. The test can be easily done using Diabetes test strips. These are disposable plastic strips which help diabetes patients in monitoring their blood glucose level. Read the instructions carefully mentioned in the box containing the test strips or in the information leaflet to do the test and check the result without any confusion.
Is there any preparation required before the test?
Some diabetes tests require overnight fasting. Otherwise, no special preparation is required. However, consult your physician regarding the preparation for your diabetes test.
How is Diabetes treated?
Regardless of the type of diabetes, blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, and physical activity play a major role in the treatment. Type 1 Diabetes can be treated with insulin therapy like insulin injections and insulin pumps. In some people, a pancreas transplant would be an option. Type 2 Diabetes can be managed with changes in the lifestyle, medications, and routine checking of blood sugar levels. Controlling the blood sugar levels with proper diet and physical activity is the only way to manage gestational diabetes and to avoid any further complications in the mother and the baby.
Normal blood sugar levels
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the normal blood sugar levels should be 80-130 mg/dL before eating a meal (fasting), and less than 180 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after eating a meal. If the blood sugar levels are higher or lower than normal, you might be at risk of getting diabetes or prediabetes.
What are the risk factors and complications of Diabetes?
The following factors can increase the risk of getting Diabetes.
- Obesity
- Above 45 years of age
- Family history of having any type of Diabetes
- Had gestational Diabetes
- Prediabetics
- High blood pressure
- High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides
- No physical activity
The following factors can increase the risk of getting gestational Diabetes.
- Obesity
- Gestational diabetes in the past pregnancy
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Family history of type 2 Diabetes
Complications of Diabetes
High blood sugar levels cause severe complications to the organs, muscles, and tissues of the body. The following are the complications associated with Diabetes.
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
- Foot damage
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Depression
- Hearing loss
- Bacterial and fungal infections
The following are the complications to the mother and baby if she has uncontrolled gestational Diabetes.
- Premature birth
- Type 2 Diabetes later
- Low glucose
- Jaundice
- Excess weight at birth
Gestational Diabetes can also lead to cesarean delivery (C-section).

How to prevent Diabetes?
A healthy lifestyle, proper low carb diet, and physical activity are the only ways to prevent Diabetes.
Provider Locations
A diabetes blood test can be done at any of our partner’s 4500+ labs located across the US. To know the diabetes blood test cost, refer to the first section of the article.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a diabetes blood test?
A diabetes blood test is a laboratory test that measures the levels of glucose (sugar) in a person’s blood. This test is used to diagnose and monitor diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels.
Why is a diabetes blood test done?
A diabetes blood test is typically done to check for diabetes, to monitor blood sugar levels in people who have been diagnosed with diabetes, and to evaluate the effectiveness of diabetes treatment.
How is a diabetes blood test done?
A diabetes blood test can be done in several ways, including a fasting blood sugar test, an oral glucose tolerance test, or a random blood sugar test. The most common is the fasting blood sugar test where you will be asked to fast for 8 to 12 hours before the test.
What do high levels of glucose in the blood mean?
High levels of glucose in the blood can indicate diabetes or prediabetes, which is a condition characterized by blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be considered diabetes.
What should I do if I have high levels of glucose in my blood?
If you have high levels of glucose in your blood, you should contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment. They may recommend lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, or medications to help lower your blood sugar levels.
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- What is Herpes? Symptoms of Genital Herpes in Women
- Symptoms of Herpes Infection in Men
- At-Home Chlamydia Testing Cost in the U.S.
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone, AMH Home Testing Kit Cost in the U.S.
- How much does the Ovarian Cancer, CA – 125 Test Costs in the U.S?
- Cost of Cancer Tests in the U.S.
- STD Test Cost in Atlanta, Georgia
- Symptoms of Gluten Intolerance
- ANA Test Cost in the U.S.
- STD Testing Cost in San Diego, California
- Types of STDs that cannot be cured
- What is Lyme Disease | Lyme Disease Testing near me
- How much does the Ferritin Test Cost in the U.S?
- Cost of Cortisol Testing in the U.S.
- Types of STDs That Cause Skin Rashes on Genitals and Body
- Causes of Penile Rashes and Other STD Symptoms in Men
- Do STDs cause Blood in Urine? Know more on Other Symptoms of STDs
- Symptoms of Gonorrhea, Causes, Transmission, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Oral STDs: Names, Symptoms, Treatment and Testing Cost






