Cancer is a deadly disease in which cells in your body grow out of control. When cancer affects your lungs, it is called lung cancer. Lung cancer begins in the lungs and spreads to the lymph nodes or other organs in your body, such as your brain. Similarly, cancer from the other organs may also spread to the lungs. When the cancer cells spread from one organ to another then they are called metastases.
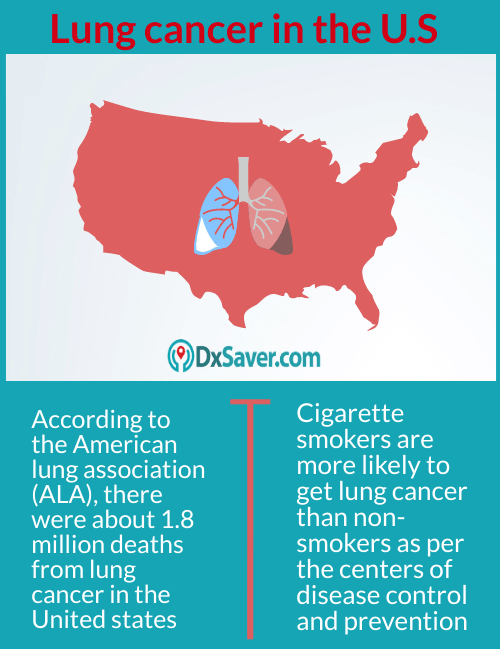
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer deaths in the United States. The lungs are two squidgy organs in the chest that helps in filtering the required oxygen while inhaling and releases carbon dioxide when we exhale. People who smoke regularly have a high risk of lung cancer, but lung cancer may also occur in those people who have never smoked. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), cigarette smokers are more likely to get lung cancer than nonsmokers. So we highly recommend every individual to get tested for lung cancer at least once in a year.
- What are lung cancer stages?
- Lung cancer types
- Lung cancer symptoms
- Lung cancer survival rate
- Is lung cancer curable?
- Lung cancer diagnosis
- Lung cancer treatment
- Prevention
- How to get tested
- Providers Locations
What are lung cancer stages?
Cancer stages help your physician know how far cancer has spread and also helps determine the treatment. The chance of successful treatment is much higher when lung cancer is diagnosed and treated at early stages before it spreads to other organs of your body. Although lung cancer doesn’t show any symptoms at earlier stages, diagnosis only comes after it has spread.
The four main stages of lung cancer are as follows:
- Stage 1: At this stage, the cancer is found in the lungs, but it has not spread outside the lungs yet.
- Stage 2: Cancer is found in the lungs and in the nearby lymph nodes at this point.
- Stage 3: Cancer is found in the lung and the lymph nodes in the middle of your chest at this stage.
- Stage 3A: Cancer is found in the lymph nodes at this stage, but it’s only on the same side of the chest where cancer first started to grow.
- Stage 3B: In the Lung cancer 3 stage, cancer has spread to the lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest or the other organs in the body.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to both the lungs in Lung cancer stage 4, into the area around the lungs, or to the distant organs.
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) has two stages. In the limited stage, cancer is found in one lung or in the lymph nodes on the same side of the chest.
In the extensive stage cancer has spread:
- throughout one lung
- to lymph nodes on the opposite side
- to fluid around the lung
- to bone marrow
- to the opposite lung
- to distant organs
Lung cancer types
Your physician divides lung cancer into two types based on the appearance of lung cancer cells under the microscope. And then your physician determines the treatment based on which type of lung cancer you have.
The two general types of lung cancer are:
- Small cell lung cancer- Small cell lung cancer occurs almost in heavy smokers and is very less common than non-small cell lung cancer.
- Non-small cell lung cancer- Non-small cell lung cancer is a term used for several types of lung cancers. This lung cancer includes squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Mesothelioma is a type of lung cancer that is usually associated with asbestos exposure. Small-cell lung cancer represents about 15 to 20 percent of lung cancers. SCLC grows and spreads faster than Non-SCLC. It also makes it more likely to respond to chemotherapy. But, it’s also less likely to be cured with treatment.
Lung cancer symptoms
Symptoms of non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer are similar. Early symptoms will include:
- Lingering or worsening cough
- Coughing up phlegm or blood
- Chest pain when you breathe deeply, laugh, or cough
- Hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
You may also have respiratory infections such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
As cancer starts spreading, additional symptoms depend on where new tumors are formed. For example, if in the:
- Lymph nodes: lumps, mainly in the collarbone or neck
- Bones: bone pain, mostly in the ribs, lips, or back
- Brain or spine: numbness in the arms or legs, headache, dizziness, balance issues.
- Liver: Jaundice, yellowing of the eye
Tumors that appear in the top of the lungs can influence facial nerves and it may lead to drooping of one eyelid, small pupil, or absence of perspiration on one side of your face. These symptoms occur together and they are called the Horner syndrome. It may also cause shoulder pain.
Lung cancer creates a substance like hormones, a wide variety of symptoms called paraneoplastic syndrome that includes:
- Weakness in the muscles
- Vomiting
- Fluid retention
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Coma
Lung cancer survival rate
According to the American Lung Association (ALA), there were about 2.1 million new cases in 2018, as well as 1.8 million deaths from lung cancer in the United States. Current survival statistics of lung cancer don’t tell the entire story. In recent years, new treatments have approved for stage 4 non-small cell lung cancers. Some people are surviving much longer than those who have undergone traditional treatments. Small-cell lung cancer is very aggressive than the other. For a limited stage, the five-year survival rate would be 14 percent and the median survival is from 16 to 24 months. Median survival for extensive-stage would be 6 to 12 months.
Long-term disease-free survival is very rare. Without the treatment, the chance of survival is only two to four months. The five-year survival rate for mesothelioma is 5 to 10 percent. In the United States, around 7,300 people who never smoked die from lung cancer each year due to passive smoke.
Is lung cancer curable?
Lung cancer can be curable if it is caught at an early stage. Regular CT scans generally promote early detection, which may allow you to get very minimal surgery and can be cured. The longer you wait, the risk is higher. That is you’re talking about major surgery and much worse outcomes. Your physician will say that lung cancer is not truly cured. However, the longer someone lives with no history of cancer, the less likely it is they’ll see the cancer return.
Improvements in the treatments of lung cancer helped many people survive.
Lung cancer diagnosis
After a physical examination, your doctor will tell you how to prepare for the tests:
- Imaging tests: An abnormal mass can be seen on MRI, X-ray, CT, and PET scans as these scans help produce more detail and find smaller lesions.
- Sputum cytology: If you produce phlegm while coughing, microscopic examination can determine if cancer cells are present in your body.
A biopsy will help determine if the tumor cells are cancerous. A tissue sample can be obtained using:
- Bronchoscopy: While under sedation, a tube with a light is passed down the throat and into the lungs, allowing closer examination.
- Mediastinoscopy: Your physician makes an incision at the base of your neck. A lighted instrument is inserted into the lymph nodes and surgical tools are used to take the samples. It’s usually performed in a hospital by an expert under anesthesia.
- Needle: A needle is inserted through the chest wall and into the suspicious lung tissue. Needle biopsy is also used to test the lymph nodes.
Tissue samples are then sent to a pathologist for analysis purposes. If the result is positive, then further testing is done, such as a bone scan, which helps determine if cancer has spread and helps identify staging.
Lung cancer treatment
Lung cancer treatment varies upon the situation of the lung cancer stages. Your physician may be able to help determine the best suitable treatment for you. Discuss all your treatment options with your physician before making a decision. They will coordinate and keep each other informed. Treatment for non-small cell lung cancer varies from one person to another person as it depends upon the specific details of your health.
Options for small cell-lung cancer may also include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. In most cases, the surgery cannot be performed as cancer must have reached the advanced stage. Some people with advanced lung cancer may not choose to continue with treatment. But you can choose palliative care treatments which help in treating the symptoms of cancer rather than cancer itself.

Prevention
There’s no accurate way to prevent lung cancer, but you can reduce your risk if you follow the above:
- Don’t smoke- If you don’t smoke, then don’t start. Talk to your children about not smoking so that they can understand how to avoid the risk of lung cancer. Begin conversations about the dangers of smoking with your children at an early age so that they can handle peer pressure.
- Stop smoking- Quitting may reduce the risk of lung cancer, even if you’ve smoked for several years. Talk to your physician about strategies that can help quit smoking. Options may include nicotine replacement products, medications, and support groups to quit smoking quickly.
- Avoid secondhand smoke- If you live or work with a smoker, tell him or her to quit. Or ask him or her to smoke outside. Avoid visiting areas where people smoke, like bars and restaurants, and seek out smoke-free options.
- Avoid carcinogens at work- Take precautions to protect yourself from the toxic chemicals at workplaces. Always wear a face mask when you work in the chemical industry. Consult your physician what more can be done to protect yourself at workplaces. If you smoke, the risk of lung damage from workplace carcinogens increases.
- Eat a diet full of fruits and vegetables- A healthy diet for you with a variety of fruits and vegetables. Food sources of vitamins and nutrients are always the best and preferable. Researchers hoping to reduce the risk of lung cancer in heavy smokers gave them beta carotene supplements which resulted in increasing the risk of cancer.
- Exercise most days of the week- If you don’t exercise regularly, start working out slowly. Try and exercise most days of the week.
How to get tested?
Lung cancer can be detected in the CEA blood test. This test is done to measure the levels of CEA in the blood. Your physician will prescribe for a CEA blood test to detect the tumor cells. This CEA test is used to diagnose Lung cancer, Gastric, Ovary, and Pancreatic cancer.
No prior appointment is required for cancer screening. You can compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. After completion of the procedure, the results will be emailed in 2 to 3 business days. We also provide doctor consultation for further treatment or any kind of medical advice.
The following table shows the lung cancer testing (CEA Test) cost at one of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
Personal Testing Lab
| Offer Price$59 |
Providers Locations
Lung cancer tests can be done in any of the following states at the provider’s location. To know the lung cancer test cost at these locations refer to the above table.
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- ESR Test Cost in the U.S.
- Anti-TPO Test Cost in the U.S.
- QuantiFERON Gold TB Test Cost
- RBC blood test cost in the U.S.
- How much does the Cervical Cancer Test Cost in the U.S?
- Sickle Cell Testing Cost
- Is Itching a Symptom of STD?
- Cost of Lymphocyte Blood Test in the US
- Why is Gonorrhea STD called “The Clap”?
- Oral STDs: Names, Symptoms, Treatment and Testing Cost
- What are the types of skin cancer? Know more about early signs, causes test cost & treatment
- Cost of Planned Parenthood STD Testing Vs. Other Labs/Clinics Near You
- What is creatinine in blood? Know more about the creatinine test cost near me
- What is throat cancer? Read more about its types, symptoms, and treatment
- What are the Causes of Breast Cancer?
- Signs and Symptoms of Oral Syphilis
- Types of STDs that cannot be cured
- Importance of hCG Qualitative Pregnancy Test
- Herpes Vs. HPV: Differences, Symptoms, and Testing Cost
- Estradiol (E2) Hormone: Normal Levels, Importance in Women Fertility and Testing Cost





