
Every human being requires an apt amount of hemoglobin content to be present in the blood for the proper functioning of the body. Hemoglobin makes the blood red in color. Hemoglobin is a protein content that transports oxygen from your lungs to other parts of your body. It also helps in removing the carbon dioxide from the blood.
MCH is expanded as Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin. MCH levels determine the average amount of hemoglobin present in the red blood cells.
- MCH Blood Test Cost
- What is the MCH in the Blood Test?
- What is MCH & Why is it Important?
- How is the CBC (MCH included) test performed?
- Is there any Preparation Required before the Test?
- Are there any risks in the CBC test?
- What does the MCH Test Result Mean?
- MCH Blood test high
- MCH blood test low
- How to improve low MCH levels in blood?
- How to reduce high MCH levels in blood?
- Providers Locations
For our readers, who are very much interested in knowing the MCH Blood test cost beforehand, we would like to begin with that section.
MCH Blood Test Cost
The MCH test is not taken individually. MCH levels are known from the Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test, which is a panel of tests that also measures WBC, RBC, Platelets, Hemoglobin & a few other blood cell components.
The cost of the CBC test ranges between $28 and $39 in different labs and facilities across the U.S. No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days. Doctor consultation is also available for further treatment or for any kind of medical advice.
The following table shows the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test cost at 2 of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
HealthLabs
| Offer Price$28 |
Personal Testing Labs
| Offer Price$39 |
Cost of CBC test cost with insurance
Many health insurance policies in the U.S. cover the cost of the complete blood count test when it is done once or twice a year. If your physician recommends you to take the Complete Blood Count test more than twice in a year, you may have to pay the medical bill out of pocket. Also, the coverage offered by private health insurance policies and national health insurance programs varies widely. So we recommend you to check with your insurance company.
Our CBC testing providers do not accept any health insurance. But, on request, they can provide you with a receipt containing all the details like the name and code of the test, and CPT code which is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
What is the MCH in the Blood Test?
MCH is measured by taking a Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test. A CBC test is done to screen for various blood-related issues at once. This test help diagnoses conditions, such as bleeding disorders, infections, and anemia. Your physician may also prescribe this CBC test to know how well the current treatment is performing.
A CBC test studies the content of all the types of blood cells in the given blood sample. They include – White Blood Cells (WBC), Reb Blood Cells (RBC) & platelets in the blood. This test is most commonly taken to examine the levels of MCH in the blood.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin, otherwise commonly known as MCH, is the average amount of hemoglobin content in one of your red blood cells.
Some people tend to confuse the MCH with other blood terms, such as –
1) MCHC – which is your “Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration”. It also calculates the hemoglobin content but it primarily focuses on the size of your red blood cells.
2) MCV – which shows the average size of the cells is Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV).
However, all are a reflection of the health of the hemoglobin in your blood.
What is MCH & Why is it Important?
MCH helps in diagnosing various health issues ranging from nutrient deficiencies to chronic diseases. For a healthy functioning of the body organs and hormones, proper oxygen supply is required throughout the body. MCH is the mean value of the hemoglobin content in each of your blood cells. Hemoglobin is a type of protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to the blood so that it reaches every end of the body through the bloodstream.
Unusually high or low levels depict that you have single or multiple diseases or blood disorders. Your doctor may look at your CBC test results, focused on MCH, MCV, and MCHC values if you show signs of anemia or other nutritional deficiencies.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin, MCH levels is arrived at the calculation based hemoglobin value (Hgb), which is the total count of hemoglobin in the blood divided by the RBC, which is the number of red blood cells in the blood, yielding an average amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell.
How is the CBC test performed?
As the name suggests, the Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a simple blood test. During this test, a lab technician or a phlebotomist will cleanse the skin with an antiseptic and place an elastic band around the upper arm so that the vein becomes visible and swells with blood. He/she then injects a needle and draws a sample of blood in a test tube. After the blood is drawn, he covers the injected area with a band-aid to stop bleeding. The typical blood specimen is then sent to the lab for analysis.
It takes less than 10 minutes to perform this test.
Is there any preparation required before the test?
There is no special preparation required for the Complete Blood Count test. But if the blood sample is going to be used for other tests, you may have to fast for a certain period. Your concerned physician will give you specific instructions on diet.
Are there any risks in the CBC test?
There is no possible risk or complication in taking the CBC test. You might have slight pain or bruise in the injected area for a very little period.
What does the MCH Test Results mean?
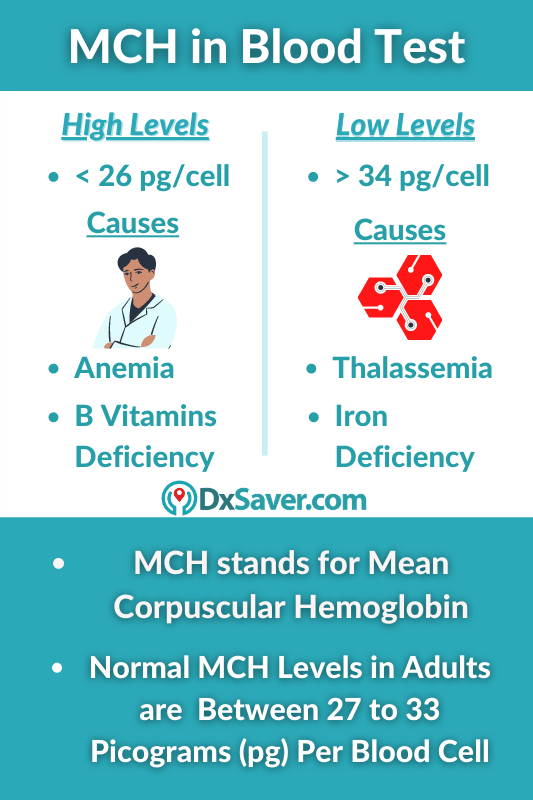
Generally, normal MCH levels should stand between 27 to 33 picograms (pg) per cell in grown adults. If the results show that MCH concentrations below 26 pg per cell, it is considered low MCH levels. When the test results of MCH levels exceed 36 pg, it is abnormally high. However the numbers differ according to age, children have different normal levels.
The abnormal levels of MCH in the blood are determined with the help of other components of the Complete Blood Count (CBC) blood test. These blood tests are done to examine the nutritional status and are helpful tools for physicians to detect any nutritional deficiencies in the body. Your physician may also order various other blood tests, depending on your exhibited symptoms to evaluate the cause of abnormally high or low MCH levels.
MCH Blood Test High
If your CBC blood test shows, MCH levels over 34 pg, then you have high MCH levels. This means that there are more than the required amount of hemoglobin present per red blood cell.
The most common reason for high MCH is macrocytic anemia, which is a blood disorder in which the body fails to produce enough red blood cells.
Causes of High MCH in Blood Test
Following are the causes of high MCH levels in your blood cells –
One of the major causes of low MCH in the blood is macrocytic anemia. In macrocytic anemia, red blood cells that are produced are larger than usual, each carrying more hemoglobin than normal-sized cells would, where the body fails to produce enough red blood cells. This type of anemia can influence heart function, early diagnosis, and treatment of macrocytic anemia is crucial. It’s more common if you’re in your old age. Lifestyle/genetic factors can also cause it. Symptoms of macrocytic anemia are:
- Heart complications
- Heart palpitations
- Unexplained fatigue
In some cases, certain medicines that are taken for the following treatments can cause your MCV and MCH levels to go high:
- Anticancer
- Antiretroviral
- Anticonvulsant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antidiabetic
- Diuretics
Following are some of the other reasons to have a high MCH test –
- Anemia
- Alcoholism
- Autoimmune disorder
- Down syndrome
- Cigarette smoking
- Chemotherapy
- Certain infections
- Deficiency of B vitamins (B-12 and folate)
- Liver problems
- Hypothyroidism
- Inability to absorb vitamin B12 (pernicious anemia)
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (a stem cell disorder)
- Overuse of estrogen-containing medications
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Vegan diet (plant foods have little to no B12)
In rare cases, the cause of high MCH levels may not know, or you may not notice any unusual symptoms causing high MCH levels. Your physician would want to know your family history to diagnose the issue and may ask you to get tested for your MCH levels every six months.
Symptoms of High MCH in Blood
If your blood cells have high levels of MCH in them, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Pale or Yellowish Skin
In the case of the anemic condition due to folate deficiency (Vitamin B-12 deficiency), you may also experience:
- Bloating and gas
- Mental symptoms (Depression or Confusion)
- Nausea or Vomiting
- Tingling in your limbs
- Diarrhea
- Decrease in appetite
- Irritability
- A smooth or sensitive tongue
How to Reduce High MCH Levels in Blood?
High MCH levels can be altered by changing some lifestyle habits and diet. The most common cause of high MCH, which is due to a shortage of B-12 can be treated by taking foods rich in vitamin b-12 and supplements of these vitamins to further boost your B-12 and folate levels or if absorption is a problem.
If you have low levels of Vitamin B-12, you may feel better within a few days of medications. It is advisable to consult your physician and get rechecked for B-12 regularly. Prolonged lack of Vitamin B1-2 can lead to stomach cancer.
MCH Blood test Low
MCH levels below 26 pg are considered low. Most of the time, low MCH is found in people who have an iron deficiency. Hemoglobin production in your red blood cells requires iron content. Your body intakes the iron content from the food. Deficiency in iron may be due to the consumption of low-iron content food, a recent major surgery, or blood loss.
Some other causes of Low MCH include blood loss, and microcytic anemia (a condition where red blood cells are abnormally small, transporting less hemoglobin)
Causes of low MCH in Blood
The following are some of the potential causes to see a low MCH count in the blood test,
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- hemoglobinopathy (disorders that cause structural change in hemoglobin)
- In more rare cases, a genetic condition called Thalassemia may lead to low MCH levels.
Thalassemia is a condition where the production of hemoglobin is limited. People who have Thalassemia have lower Reb Blood Cells circulating in the blood.
Symptoms of Low MCH in blood
If you suspect you are short of MCH levels in your blood, then check for the following symptoms –
- An urge to eat ice or clay
- A hard time focusing
- Chest pain when you are active
- Headache
- Fast heartbeat
- Leg cramps
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath
- Strange noises in your ears
- Tiredness
- Tongue problems (soreness or smoothness)
- Weak nails or hair loss
How to improve low MCH levels in blood?
Low MCH caused by iron deficiency. You can include iron-rich foods to your diet or taking iron supplements can help boost the MCH levels in the blood.
If you have a mild lack of iron, you can increase the iron content by:
- Taking an iron-rich diet
- Iron supplements
- Adding vitamin C to your diet (to help you absorb iron)
- Avoid drinking black tea (lowers iron absorption)
In rare cases, such as when symptoms are severe, a serious lack of iron or blood loss has occurred, you may need
- Intravenous (IV) iron therapy – (iron medications are directly injected into a vein)
- A blood transfusion (a donor’s blood infused into your vein)
People with mild thalassemia may not require treatment. However, blood transfusions may be required if your symptoms are severe.
- Blood transfusions
- Iron chelation therapy – medication that you swallow or receive via IV, which you may need if you have high iron from many transfusions
- Folic acid supplements
Providers Locations
The MCH test can be done in any of the following locations across the U.S. by visiting the nearest lab. To know the MCH test cost, refer to the first section of the article.
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order anytime before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- STDs that Cause Blood in the Urine
- Hepatitis C – Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
- Testosterone Test Cost
- Quantiferon TB Gold Test Cost in the US
- How much does a CT Scan Cost in the US?
- What is GGT Blood Test & its Importance?
- Is Itching a Symptom of STD?
- Anti-aging Testing Cost in the US






