
Our body needs minerals to function properly and to stay healthy. Minerals are divided up into major minerals and trace minerals. Generally, a balanced diet provides all of the essential minerals. Mineral deficiency occurs when the body does not absorb or obtain the required amount of a mineral. The five main categories of mineral deficiency are iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and zinc. And minerals can be obtained from food or mineral supplements.
This article covers all the significant topics related to the mineral deficiency test such as the test cost, types, symptoms, causes, and how to get tested for a mineral deficiency test.
- What are minerals?
- Mineral deficiency
- Types of mineral deficiency
- Causes of mineral deficiency
- Mineral deficiency symptoms
- Mineral deficiency test
- What happens during the mineral deficiency test?
- Risk of mineral deficiency test
- Mineral deficiency treatment
- Provider locations
For our readers who are interested in knowing the mineral deficiency test cost beforehand, we begin with that section.
How much does the mineral deficiency test cost?
Mineral deficiency test costs range around $349 in different labs and facilities across the US. Prior appointment isn’t required. You can order tests online by comparing the price or visiting the nearest lab during lab business hours. You will get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days after completing the procedure. Apart from this, doctor consultation is available for any kind of further treatment or medical advice.
The table below shows the mineral deficiency test provider and their prices. You can know more and book the test by clicking on the “Book Now” button. All the labs are certified and offer a network across the US.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online at Offer Price |
HealthLabs
| $349 |
Mineral deficiency test cost with insurance
Many insurance companies in the U.S. cover all the vital tests like a mineral deficiency test. However, the coverage provided by private health insurance companies and national health insurance programs like Medicare varies widely. Most of the health insurance policies cover mineral deficiency test costs only once or twice a year and when your physician orders more than twice in a year, you should pay the test cost out of pocket. So, you are recommended to check if your health insurance policy covers the mineral deficiency test cost.
Our mineral deficiency testing providers do not accept any kind of health insurance policy. However, they can provide you with an itemized receipt containing all the details viz the name of the test, code of the test, and CPT code which is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
What are minerals?
Minerals are certain kinds of nutrients that the body needs to function properly and to stay healthy. The body uses minerals for many jobs, including keeping the muscles, bones, heart, and brain working properly. They are also important for making enzymes & hormones.
There are two kinds of minerals:
- Macrominerals
- Trace minerals
The amount you need differs between these minerals. Generally, major or macro minerals are required in larger amounts. They include calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chloride, magnesium. Trace minerals or microminerals are important for bodily functions but are required in smaller amounts. Trace minerals include iron, manganese, iodine, zinc, copper, cobalt, fluoride, and selenium. Usually, a balanced diet provides all of the essential minerals and most people get the minerals they need by eating a wide variety of foods.
Mineral deficiency
Mineral deficiency occurs when the body does not absorb or obtain the required amount of a mineral. Your body requires different amounts of each mineral to lead a healthy life. These minerals can be obtained from food, mineral supplements, and food products that have been fortified with extra minerals. Generally, mineral deficiency happens slowly over time. And the deficiency can also be caused by various factors, like an increased need for the mineral, lack of the mineral in the diet, or difficulty absorbing the mineral from food. This deficiency can lead to various health problems like a decreased immune system and weak bones.
Types of mineral deficiency
Calcium deficiency
Calcium is necessary for every cell in your body. It mineralizes bones & teeth, especially during times of rapid growth. And it serves as a signaling molecule. Calcium supports the proper function of your blood vessels, muscles, nerves, and hormones. Severe calcium deficiency occurs due to medical issues or treatments, like surgery to remove the stomach, kidney failure, or medications like diuretics.
Signs of a severe deficiency may include:
- Numbness
- Tingling in the fingers
- Cramping of the muscles
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Poor appetite
- Tiredness
However, it is best to get calcium from food rather than supplements. Because they seem to benefit people who are not getting enough in their diet. Supplements can increase the numbers slightly, but still, most people were not getting enough calcium. Natural sources of calcium include milk and milk products, small fish with bones, beans, and peas. Other sources include almonds, bok choy, parsley, watercress, greens (broccoli, mustard greens), kale, and Chinese cabbage can provide calcium. And fortified tofu or fortified soy milk can also provide calcium.
Low calcium intake is very common in women of all ages and older adults. The main symptom of this calcium deficiency is an increased risk of osteoporosis. Over the long term, it can lead to decreased bone mineral density called osteopenia. When it is left untreated, osteopenia can turn to osteoporosis and it can increase the risk of bone fractures.
Iron deficiency
Iron is an essential mineral and a large component of red blood cells (RBC), in which it binds with hemoglobin and transports oxygen to your cells. It is also a part of other enzymes and proteins that keep your body healthy. Iron deficiency anemia takes place when your body does not have enough iron to produce hemoglobin. When you aren’t taking enough iron, or if you’re losing too much iron, your body can’t produce enough hemoglobin and this will lead to iron deficiency anemia.
The symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia may include:
- Extreme fatigue
- Pale skin
- Chest pain or fast heartbeat or shortness of breath
- Headache or dizziness
- Cold hands and feet
- Brittle nails
- Unusual cravings
Food rich in iron may include red meat, poultry, and pork, seafood, beans, peas dark green leafy vegetables (spinach), dried fruit (raisins and apricots), iron-fortified cereals, bread, and pasta.
Magnesium deficiency
Magnesium is a key mineral in the body and is involved in more than 300 enzyme reactions. It is also important for bone and tooth structure. Additionally, the proper function of muscles and nerves, brain function, energy metabolism, and protein production are also controlled by magnesium. This deficiency is rare in healthy people. The kidneys keep magnesium from leaving the body via urine. However, certain medications and chronic health conditions (like alcoholism) can also cause magnesium deficiency. Magnesium needs are influenced by the presence of disease and in such cases, the recommended daily allowances (RDA) may not be sufficient for some people.
Early signs of magnesium deficiency may include:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
The symptoms of severe magnesium deficiency may include abnormal heart rhythm, muscle cramps, restless leg syndrome, and migraines. Whereas ore subtle, long-term signs that you may not notice are insulin resistance and high blood pressure.
Food sources of magnesium include legumes, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and green leafy vegetables like spinach.
Potassium deficiency
Potassium is a mineral and it functions as an electrolyte. The body needs potassium for muscle contraction, proper heart function, and the transmission of nerve signals. The most common cause of this deficiency is excessive fluid loss. Certain conditions like kidney disease, overuse of diuretics, magnesium deficiency, use of antibiotics, like carbenicillin and penicillin can cause potassium deficiencies or hypokalemia.
Symptoms of potassium deficiency include
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Muscle Cramps and spasms
- Tingling and numbness
- Breathing difficulties
- Mood changes
Food sources of potassium are fruits and vegetables, like bananas, avocado, dark leafy greens, beets, potatoes, and plums. Other sources may include orange juice and nuts.
Zinc deficiency
Your body used zinc for fighting off infections and producing cells. Zinc is also essential for healing injuries and creating DNA, the genetic blueprint in all of your cells. It is important for proper growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence. Although zinc deficiency is rare in the US, it still occurs in a few people.
When you’re zinc deficiency, you may experience symptoms like:
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Decreased sense of smell & taste
- Wounds that won’t heal
- Lack of alertness
- Open sores
Food sources of zinc may include animal products like oysters, red meat, and poultry. Other sources are beans, nuts, whole grains, and dairy products.
Causes of mineral deficiency
When a person is not getting enough minerals from food or supplements it can lead to a mineral deficiency. Different types of diets can lead to a mineral deficiency. For instance, a diet that depends on junk food, or a diet that lacks adequate fruits and vegetables can also result in this deficiency. A very low-calorie diet may also cause mineral deficiency. It includes people in weight-loss programs or with eating disorders. Additionally, older adults with poor appetites may not get enough nutrients in their diet. People with food allergies or lactose intolerance and vegetarians, vegans may experience mineral deficiency when they fail to manage their diet in an effective way.
Difficulty with the digestion of food or absorption of nutrients can lead to this deficiency. Causes of these difficulties may include chronic alcoholism, surgery of the digestive tract, diseases of the liver, gallbladder, intestine, pancreas, or kidney, or medications like antacids, antibiotics, laxatives, and diuretics. Apart from this, mineral deficiency can also result from an increased need for certain minerals. Women may encounter this need during pregnancy, heavy menstruation, and post-menopause.
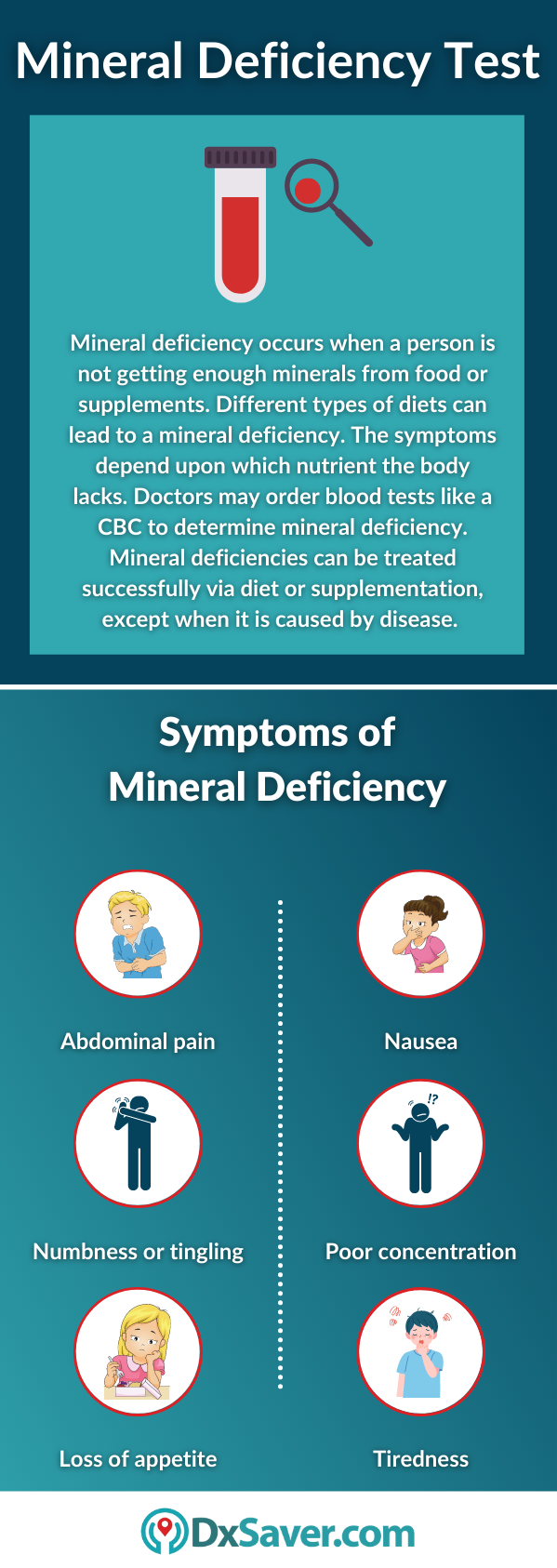
Mineral deficiency symptoms
The symptoms depend upon which nutrient the body lacks. Some symptoms may be mild, so they go unnoticed. Symptoms may include:
- Weakness or tiredness
- Muscle cramping
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Constipation, bloating, or abdominal pain
- Decreased immune system
- Irregular heartbeat
- Nausea and vomiting
- Poor concentration
- Slow social or mental development (in children)
As the symptoms may be a sign of another health condition, it is important to consult a doctor.
Mineral deficiency test
Your doctor may check your medical history, including symptoms and family history of diseases, and conduct a physical exam or review of your diet and eating habits. Doctors may order blood tests like a complete blood count or CBC and a measure electrolyte (minerals) in the blood to determine if you have a mineral deficiency.
Underlying conditions are also a factor. Your doctor may order additional tests to identify the amount of damage before deciding on a treatment plan. It can include treatment for other diseases or a change in medication.
What happens during the mineral deficiency test?
A mineral deficiency test requires a blood sample. Your healthcare professional or lab tech will take the blood sample from a vein in your arm. So, they will tie a band around the upper part of the arm to make the vein fill with blood and swell up. And they will clean the area with an antiseptic and place a needle into the vein, you may feel a slight prick or stinging sensation when the needle goes in or out. After collecting the sample in a test tube, a healthcare professional will remove the needle and the band. And they will put gauze or bandage over the area where the blood was drawn.
Risk of mineral deficiency test
There is little risk in having a mineral deficiency test. You may experience slight pain or bruise in the area where the needle was inserted. But the symptoms go away quickly.
Mineral deficiency treatment
Mineral deficiencies can be treated successfully via diet or supplementation, except when it is caused by disease. And the mineral deficiency treatment depends upon the type and the severity. The treatment for fluid imbalances & related deficiencies in calcium, sodium, potassium, and phosphate need intravenous (IV) infusion of the deficient mineral in fluid over a while. In the case of children, they are given oral pediatric preparations to restore fluids and minerals.
Iron deficiency may require oral supplementation or injectable iron and vitamin C helps to assimilate iron. Whereas iodine deficiency can be treated and prevented by consuming foods fortified with iodine like table salt. For magnesium deficiency, a magnesium-rich diet will be recommended. But when the deficiency is due to prolonged depletion doctors may recommend injections of magnesium sulfate. Copper and zinc deficiencies can be treated with supplementation.
You may require a multivitamin or mineral supplement because certain mineral deficiencies can’t be treated with diet alone. These supplements may be taken alone or with other supplements that help the body absorb or use the mineral. For instance, vitamin D is taken along with calcium. Your doctor will decide how much and how often you should take supplements. It is important to note that excessive intake of supplements can also be harmful, so it is essential to follow your doctor’s instructions.
Your doctor will order additional blood tests to determine whether the treatment was successful.
Provider locations
A mineral deficiency test can be done in any of the following locations by visiting the lab near you. To know the mineral deficiency test cost, refer to the first section of the article.
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you with a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order any time before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may also be interested in:-
- What is Ammonia in Blood?
- Causes and Symptoms of Zika Virus
- What is CoQ10?
- Glucose Blood Test: Purpose, Procedure and Test Results
- Arsenic Blood Test – Causes, Symptoms & Treatment of Arsenic poisoning
- Bioidentical Hormone Test: Benefits, and Test Cost
- What is the Myasthenia Gravis Test?
- Symptoms of Ovulations and Testing Cost
- What is a Titer Test?
- How much does Pancreatic Cancer Testing Cost in the US?
- What is GGT Blood Test and its Importance?
- Importance of Aldosterone to Renin Ratio
- Symptoms of Trichomoniasis STD
- Importance of BNP Levels in Blood
- AST Blood Testing Cost in the US
- Can you get STD from a Toilet Seat?
- Anti-aging Testing Cost in the US






