
Do you know that prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in American men? According to the American Cancer Society, an estimated number of 191,930 new prostate cancer cases will be diagnosed and 33,330 men diagnosed with prostate cancer will die in the U.S. in the year 2020. Prostate cancer can be cured only when it is diagnosed and treated at an earlier stage. Most of the men affected with prostate cancer do not show any symptoms at an earlier stage. So we highly recommend every man to get tested for prostate cancer screening test or PSA test (prostate-specific antigen test) at least once every two years.
The article covers all the important topics related to prostate cancer like prostate cancer screening test cost or PSA test cost, causes of prostate cancer, different types, early signs and symptoms, stages of prostate cancer, prostate cancer treatment and prevention, and how to get tested for prostate cancer screening test.
- PSA test cost
- What is prostate cancer?
- What are the causes of prostate cancer?
- Different types of prostate cancer
- What are the early signs of prostate cancer?
- How is the prostate cancer diagnosed?
- What are the 4 stages of prostate cancer?
- What is the treatment of prostate cancer?
- Is there any side-effect in prostate cancer treatment?
- Is prostate cancer curable?
- Prostate cancer prevention
- Providers locations
For our readers, who are more interested in knowing the prostate cancer screening test cost or PSA test cost beforehand, we would like to begin with that section.
How much does the PSA test cost?
PSA test costs $53 in the U.S. To view and compare the prices in different labs offered by different providers, click the button below. No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days.
The following table shows the PSA test cost at one of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
Personal Testing Lab
| Offer Price$53 |
Prostate cancer testing
Testing for prostate cancer is a two-step process.
1. Prostate cancer screening test (PSA test): PSA (prostate-specific antigen) blood test is done to detect the presence of cancer cells in the prostate gland. The screening test results have a positive or negative outcome.
2. Prostate cancer advanced testing: When the PSA test results are positive, some advanced diagnostic tests like biopsy and digital rectum exam will be ordered by your physician to know the exact stage of the prostate cancer.
PSA test cost with insurance
Most of the health insurance policies in the U.S. cover the cost of both the prostate cancer screening blood test (PSA test) and advanced diagnostic tests. However, the coverage offered by private health insurance policies and national health insurance programs like Medicare and Medicaid varies widely. So we recommend you to check the coverage of your plan with the insurance company before getting tested.
Our prostate cancer testing providers offer the screening test, PSA blood test at the lowest cost, and do not accept any health insurance. But, if the insurance company accepts to reimburse the PSA test cost, they can provide you with an itemized receipt containing all the details like the name and code of the test, and CPT code that is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.

What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men in the United States. It happens when abnormal cells grow in the prostate gland, multiply rapidly, and form a tumor. The prostate is an important part of the male reproductive system. It is a small gland located below the bladder and it produces seminal fluid. The prostate gland helps in the nourishment and transportation of sperm.
Prostate cancer is a major health concern for men in the US. Generally, this cancer grows slowly without showing any symptoms. When it is diagnosed at an early stage, there are higher chances of survival. While cancer starts spreading beyond the prostate to other parts of the body, it cannot be cured. This condition is called metastatic prostate cancer.
What are the causes of prostate cancer?
It is not clear what causes prostate cancer to date. But doctors have discovered some of the following risk factors that increase the chances of prostate cancer.
- Older age
- Diet contribution (Men eating red meat are at higher risk)
- Inherited gene mutations
- Family history of prostate cancer
- Obese men
- High levels of testosterone (testosterone speeds the growth of prostate cancer)
Different types of prostate cancer
There are different types of prostate cancer mentioned below. The type of prostate cancer depends on the type of cell from where cancer started. This helps your physician to decide the treatment.
1. Adenocarcinoma
This type of prostate cancer is very common. It develops in the gland cells lining the prostate gland.
2. Ductal adenocarcinoma
This type of cancer grows and spreads quicker than others. It develops in the gland cells lining the tubes or ducts of the prostate gland.
3. Transitional cell/urothelial cancer
This type of cancer starts in the bladder and spreads to the prostate. It develops in the cells lining the tube that carries urine outside of the urethra.
4. Squamous cell cancer
This type of cancer develops in the flat cells covering the prostate gland.
5. Small cell prostate cancer
This type of cancer is also known as neuroendocrine tumors/carcinoids. These tumors start in the digestive tract and then slowly move to other parts such as the prostate. These develop in the small round cells.
What are the early signs of prostate cancer?
Most men with prostate cancer do not show any signs or symptoms in their early stages. But the prostate cancer may also be accompanied by some urinary symptoms that are usually ignored. Some of the urinary symptoms are
- Burning sensation or pain during urination
- Urge to urinate mostly at night
- Difficulty in urinating
- Weak flow during urination
- Blood in urine
- Loss of bladder control
Other than urinary symptoms, men with prostate cancer may experience the following symptoms also.
- Back pain
- Pain in the pelvis
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in the semen
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Irregular bowel habits
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain/pressure in the rectum
These symptoms do not mean that you have cancer. Other diseases like prostatitis (enlarged prostate gland) can also cause similar symptoms and this disease is very common. But we highly recommend consulting a physician immediately when you experience these symptoms for a significant period of time.
How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
Generally, screening tests like the PSA test are done to detect prostate cancer in case of people not showing or experiencing any symptoms. The following are the tests used most often to detect prostate cancer.
1. Prostate-specific antigen test (PSA blood test)
PSA blood test is a simple test taken using the blood sample that measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Because usually men with prostate cancer, have higher levels of PSA. Higher levels of PSA may indicate prostate infection, inflammation, enlargement or cancer.
PSA with DRE (Digital rectal exam) helps the physicians to diagnose prostate cancer in its earlier stages.
2. Digital rectal exam (DRE)
During this Digital rectal exam (DRE), the physician inserts his gloved fingers into the rectum to examine the prostate that is located near the rectum. If he finds any abnormalities in the shape, size, and texture of the prostate, he may order other imaging tests for further diagnosis.
3. Trans-rectal ultrasound (TRUS)
During trans-rectal ultrasound, a small probe is inserted into the rectum to examine the prostate gland. The probe emits the sound waves that help to get a clear image of the prostate gland. This ultrasound is mostly suggested when you have a high PSA level or abnormal DRE result.
In addition to the above-mentioned tests, your physician might also recommend some other imaging tests like MRI TRUS fusion, CAT scan, and prostate biopsy (prostate biopsy is a procedure where the small samples of the prostate are taken and examined under the microscope) for accurate diagnosis and correct treatment.
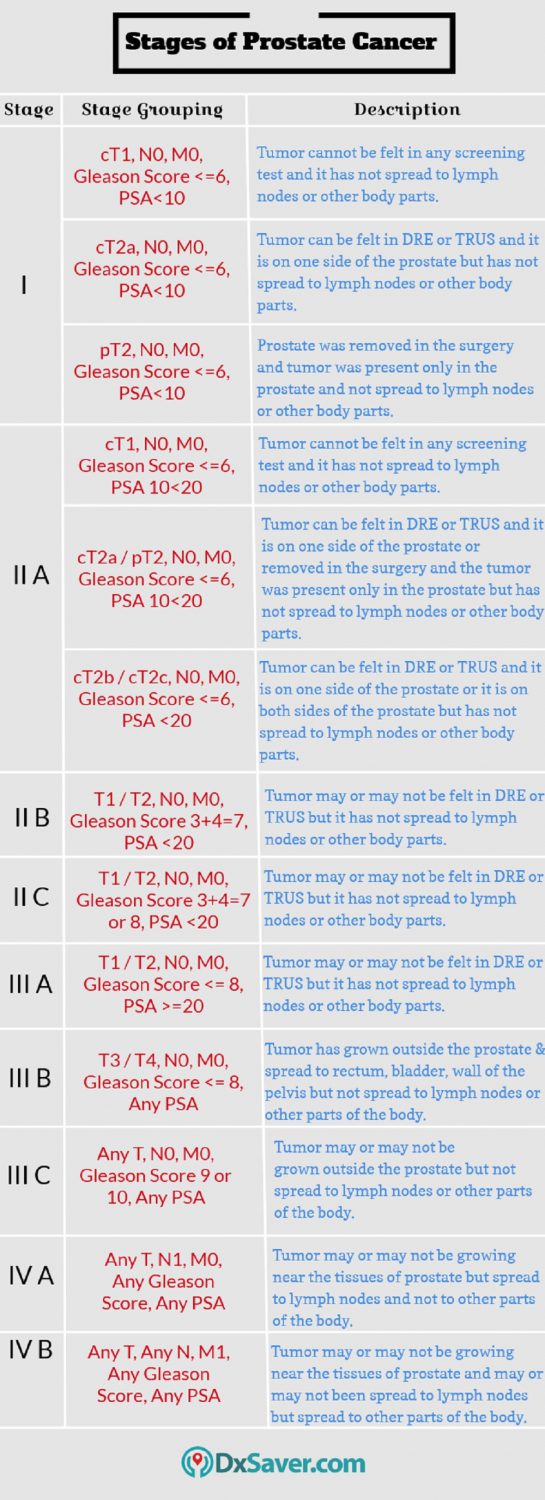
4 stages of prostate cancer
There are 4 stages (stage 1 to stage 4) of prostate cancer. To determine the stage of prostate cancer, most physicians use the TNM staging that helps them to describe different aspects of cancer’s growth.
Category T – Tumor – measures the size and the extent of tumor growth. There are 2 types of T categories.
1) Clinical T (CT) – Based on the results of the physical exam (Digital rectal exam).
2) Pathologic T (pT) – Based on the results of surgery. pT is more accurate than cT as the prostate is tested in the lab.
Category N – Node – measures the extent of cancer in the lymph nodes.
Category M – Metastasis – measures whether cancer has spread to other body parts.
After categorization, physicians combine the TNM score with your Gleason score, and PSA levels assigning a specific stage to your cancer. Gleason score is the measure of how likely the prostate cancer grows and spreads quickly. This score is determined by the biopsy results.
Various stages of prostate cancer are clearly explained in the below info-graphic.
What is the treatment of prostate cancer?
Once you have been diagnosed with prostate cancer, your physician will decide the treatment depending on the stage and grade of prostate cancer. Most often, you will have several treatments at the same time. The following are the key treatments done to treat prostate cancer.
1. Surgery
Surgery is the most common method for treating prostate cancer at its initial stage when cancer has not spread to other parts. During the surgery, the entire prostate gland is removed. This is known as radical prostatectomy. Other surgical procedures like the removal of lymph nodes will also be chosen when prostate cancer has reached its advanced stages.
2. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high energy beams (like X-rays) to destroy the cancerous cells. It is generally preferred for older men or men with some health problems. There are two types of radiation.
1) External – A machine outside the body directs the energy beams at the cancerous cells.
2) Internal (Brachytherapy) – The physician does the surgery and places the radioactive seeds into or near the cancerous cells.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses chemicals or drugs to kill prostate cancer cells. This treatment is generally used after surgery to kill the remaining cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can either be taken orally or injected into the bloodstream. This treatment is preferred only when cancer has reached the advanced stage and spread to other body parts.
4. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a rare treatment for prostate cancer. If the cancer is in its early stages, then the physician might choose this therapy to kill the cancerous cells by freezing them. But this is not the first treatment option that the physician recommends.
5. Cancer vaccine
This treatment is preferred when hormone therapy is not working. This vaccine is custom-made and helps the immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Scientists believe that this prostate cancer vaccine helps men live longer with cancer.
6. Hormone therapy
Male sex hormones called testosterone are required for prostate cancer cells to grow. Physicians call this therapy as androgen deprivation therapy where they lower the levels of testosterone and prevent the cancer cells from getting them.
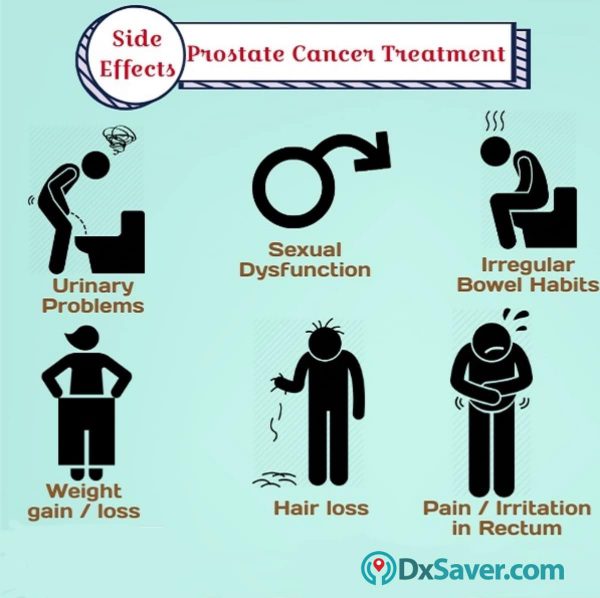
Are there any side-effects in prostate cancer treatment?
Prostate cancer treatment leads to a wide range of side effects. Consult your physician immediately when you start noticing them. Though they cannot be completely cured, they can be controlled with some medications. The following are some of the side effects caused due to prostate cancer treatment.
- Urinary problems
- Incontinence (urine leakage) while coughing, sneezing or laughing
- Impotence
- Bladder and rectal irritation
- Hormonal changes
- Erectile dysfunction
- Bowel dysfunction
- Anemia
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss or weight gain
Is prostate cancer curable?
Prostate cancer can be cured only when it is diagnosed and treated at an early stage. When cancer has spread to other parts (metastatic prostate cancer), it is very hard to cure and it can be controlled only by the hormonal treatment.
Prostate cancer prevention
To date, there is no proven strategy for prostate cancer prevention. But there are certain factors that may lower the risk of getting prostate cancer. They are
- Choose a low-fat diet – Men who eat a high amount of fat have a higher chance of getting prostate cancer.
- Healthy weight – Men who are obese have an increased risk of getting prostate cancer.
- Stop smoking – Prostate cancer patients should stop smoking as it may result in the recurrence of cancer.
- Regular exercise – Exercising daily keeps the body fit and slows down the spread of prostate cancer.
Provider Locations
The prostate cancer screening tests can be done in any of the following locations across the U.S. by visiting the nearest lab. To know the PSA test cost, refer to the first section of the article.
- Alabama
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order anytime before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may be interested in:-
- Symptoms of Herpes Infection in Men
- What are STDs symptoms? – What STDs cause dry skin?
- STD Testing Cost in Denver
- Is Bruising a Symptom of STD?
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone Test Cost in the U.S.
- How much does the Ovarian Cancer, CA – 125 Test Costs in the U.S?
- Cost of Cancer Tests in the U.S.
- STD Test Cost in Atlanta, Georgia
- Do STDs Spread Via Kissing?
- Eye Chlamydia Symptoms
- STD Testing Cost in San Diego, California
- What is Lyme Disease?
- How much does the Ferritin Test Cost in the U.S?
- Cost of Cortisol Testing in the U.S.
- At-Home Chlamydia Testing Cost in the U.S.
- Complete Blood Count, CBC Testing & Test Results Interpretation
- How Much Does At-Home COVID-19 Home Test Kit Cost in the U.S?
- Oral STDs: Names, Symptoms, Treatment and Testing Cost
- Causes of Penile Rashes and Other STD Symptoms in Men
- LDH Hormone Normal Levels, Abnormal Levels Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment





