In this detailed article, we will cover all you need to know about the Clap STD. First things first, “what is the Clap?”
The Gonorrhea sexually transmitted infection (STI) is also commonly referred to as “the clap” or “the drip”.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in the year 2018, around 583,405 new cases of the clap disease have been reported in the U.S.
It is a highly contagious infection transmitted via unprotected sexual contact with the infected person and shows almost no symptoms in its early stages.
The article below covers all the significant topics related to the clap infection. Below is the table of contents for your reference:
- What is the clap?
- Is clap an STD?
- Why is Gonorrhea STD called the clap?
- What is the prevalence of clap in the US?
- What are the symptoms of the clap?
- Is clap curable?
- What can I do to prevent getting clap?
- Can clap make me sterile?
- What does the clap look like?
- Can I get the clap from a toilet seat?
- Will I get urine in the blood with the clap?
- How can I get tested for clap?
- Is there a home test kit available?
What is the clap?
The clap is a very common Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) among young women and men in the United States.
There are many different theories about how this name came about and it is believed to be prevailing since the 15th century. One, it could refer to clapping, or throbbing hard on both sides of the penis could expel the pus secreted due to gonorrhea infection. Others believe “the clap” to be a short version of the French term “clapier” (which means “brothel”) where a great number of people likely contracted the infection back in the day.
It is also commonly referred to as “the drip” which refers to the genital discharge which is one of the main symptoms of the clap infection.
Charming names for this bacterial infection don’t stop there. Many of the STDs’ nicknames like “the clap” for gonorrhea, “Hi-Five” for HIV, and “the clam” for chlamydia are persuasive due to the social stigma around talking about them.
Is clap an STD?
The clap also referred to as “Gonorrhea” is the second most sexually transmitted disease reported in the U.S. The clap STD is caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus. The clap STD is highly contagious and has a high probability of spreading the infection to others by anal, vaginal, or oral sex and sharing unwashed sex toys. As the Neisseria Gonorrhoeae bacteria cannot sustain the physical environment outside the human body, it cannot be spread through casual contact like touching or sitting on the toilet seat.
A pregnant woman with the clap STD can pass on the infection to her newborn child at birth as the infant is exposed to the blood of the mother in a vaginal delivery. C-section birth cannot transmit gonorrhea from the infected mother.

Why is Gonorrhea STD called the clap?
Gonorrhea infection has been called the clap for several centuries. While it is difficult to ascertain the exact reason, there are a few interesting theories regarding the origin of this name.
1) French term “clapier” (means “brothel”)
“The clap” is believed to be originated from an ancient French (back in the 1580s) word “clapier” meaning “brothels”. Prostitutes lived in clapiers (brothels). In French, the word “clapier bubo” means an infection in the groin area of the penis received from visiting a brothel. Later on, the word just became the clap.
Another theory is that in the 1500s the word clap meant a rabbit’s hutch or cage. Since rabbits have a very active sex life, the hutch came to be equated to brothels where, of course, there is a lot of sexual activity. So the brothels were called the clap and the disease Gonorrhea, which was acquired from a brother came to be called the Clap.
2) Early English word “Clappen”
Another theory assumes that the birth of the term ‘clap’ is from a prehistoric English word “Clappen” which means to beat or to throb. It generally refers to the common symptoms of STDs like a burning feeling during urination, pain, swelling, and a throbbing sensation of the penis caused by inflammation and infection within the penis or vagina caused by Gonorrhea infection.
3) Clapping or throbbing against the penis
This theory refers to the supposed treatment in medieval times when someone got a Gonorrhea infection. One of the common symptoms of the disease is the accumulation of pus in the penis. The theory goes that the treatment prescribed was to clap hands vigorously with the penis in between. This was supposed to forcefully eject the pus out of the penis. This clapping theory has most likely gained popularity due to its disgusting nature.
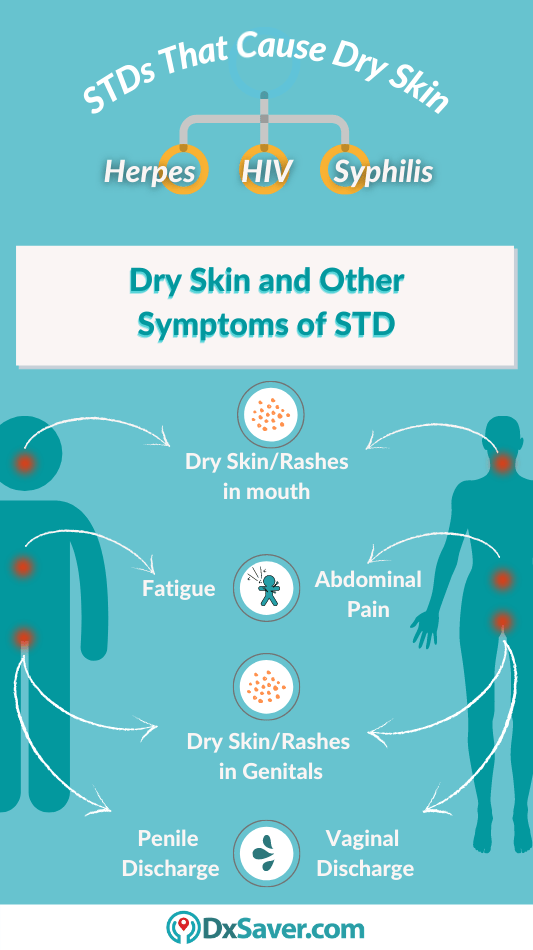
What are the symptoms of Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is generally asymptomatic for several days after exposure to the bacteria. Symptoms may start to appear one or two weeks after the infection has been contracted. Most of the symptoms are common for both men and women. However, women experience some specific symptoms apart from the common signs.
Symptoms Common for Men and Women
Gonorrhea discharge: Abnormal discharge from the vagina or penis that may be green, yellow, or white. It is commonly known as “the drip”.
Burning sensation while urinating: Also, known as dysuria, this symptom is also common with other STDs and is an important sign to get tested.
Pain, burning, and swollen glands in the throat: Burning sensation in the throat is a common symptom of various other STDs transmitted via oral sex like Oral Chlamydia.
Itching: Itching, redness, and general discomfort in the affected area.
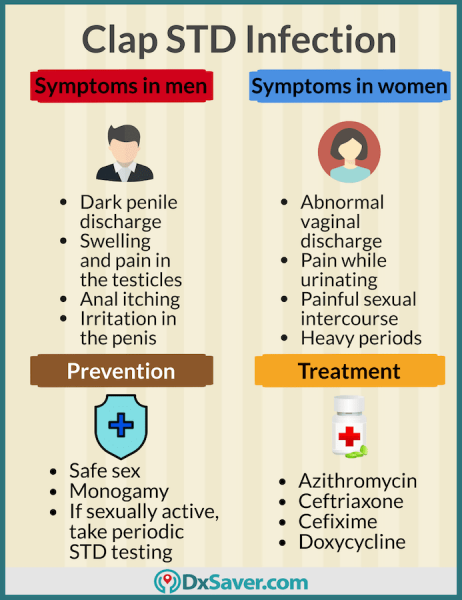
Gonorrhea symptoms specific to men
- Swollen testicles
- Inflammation around the penis
Gonorrhea symptoms specific to women
- Severe abdominal and back pain
- Bleeding during sexual intercourse
- Heavy periods and bleeding between periods
- Swelling in the vulva (outer part of the vagina)
When the clap bacterium has penetrated the bloodstream, both men and women can also encounter arthritis, heart valve damage, or inflammation of the lining of the brain or spinal cord. These conditions are rare but serious. Eventually, it can become life-threatening if left untreated.
Is clap curable?
Yes, the clap, the gonorrhea STD is curable. But, the challenging task before curing is to recognize the infection in the first place. And the prescription of treatment is not possible until you’ve taken a test. Most of the time, genital gonorrhea is tested by a urine sample or cotton swab. The cotton swab takes the sample of discharge and cells from the infected area either in the vagina, penis, anus, throat, or urethra. Men are usually asked for urine samples. The collected sample is then sent to the lab for analysis.
As the clap STD is caused by a bacterial infection, it can be cured by oral antibiotics.
Taking charge of your health and getting tested sooner rather than later so you don’t risk experiencing any of the potential complications that untreated gonorrhea can cause. The best move is to test early and test often so that, you can have peace of mind knowing if you do or do not have an STD.
How do I get tested for Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea test cost ranges between $49 and $99 in the different labs and facilities across the US. No prior appointment is required. Compare the price, order your test online and visit the lab near you during lab business hours. Complete the procedure and get the results in your email in 2 to 3 business days.
The following table shows the Gonorrhea home test kit and Gonorrhea test cost at 3 of our partner laboratories (CLIA – Certified) network located across the U.S.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online |
STD Check Labs
| Starting from
$49 |
LetsGetChecked(Home Test Kit)
| Starting from
$74.25 |
HealthLabs
| Starting from$59 |
Antibiotics for Gonorrhea STD
Gonorrhea infection has historically proven that it has become resistant to antibiotic treatments. In the 1970s, Doctors used penicillin to disinfect gonorrhea until then they found out to be no longer effective, other antibiotics came in as medications. Today, the current recommended medications and treatments are said to cure 99.2% of all genital and anal infections and 98.9% of all throat infections.
Some strains of gonorrhea STD in the US have become antibiotic-resistant, sometimes called “super gonorrhea”. Thus, a medical physician will decide on the best combination of antibiotics. You should never stop taking medications until the prescribed course is completed, even if you feel better and think the infection has been cured. If you do not finish the antibiotics, the infection can return, and be resistant to the antibiotics you were taking. The CDC recommends taking a single dose of Azithromycin (the brand name is Zithromax) and a single dose of Ceftriaxone. Other recommended antibiotics are cefixime and doxycycline.
Your doctor may ask you to do the follow-up test after two weeks to ensure you have completely got rid of the infection and you should wait seven days after finishing all the antibiotics before having sex.
What can I do to prevent getting the clap STD?
Any sexually active person can get infected through unprotected sex. The only way to prevent STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can try practicing the following steps to reduce the chances of getting the clap STD:
- Practicing monogamy – do not have sex with strangers or people other than your husband/wife
- Regular screening for STDs
Although these methods of protection aren’t bulletproof, they will definitely prevent or lower the chances of getting an STD.
Can clap make me sterile?
If the clap STD is left untreated, it can result in permanent health problems in both women and men.
In a female, untreated gonorrhea can result in PID (pelvic inflammatory disease). Some of the complications of PID are
- Infertility (inability to get pregnant)
- Formation of scar tissue that blocks fallopian tubes
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the womb)
- Long-term pelvic/abdominal pain.
In men, the clap can cause a painful condition in the tubes attached to the testicles. In rare cases, this may cause men to become impotent. Untreated gonorrhea may also increase your chances of getting affected with HIV resulting in AIDS.
What does the clap look like?
Most of the time people ask STD-related queries with the suffix “look like” and “smells like”. Unfortunately, it may not look like anything when it comes to the clap STD, it keeps a low profile and doesn’t show any presence or signs in the early stage. However, symptoms like abnormal vaginal or penile discharge, painful, burning, swollen glands in the throat, and dysuria (burning sensation while urinating) are some of the signs that show you have been affected by the clap infection.
Can I get the clap from the toilet seat?
As Gonorrhea is a Sexually Transmitted Infection, the bacterium cannot adapt to environmental conditions outside the human body even for a few seconds, the bacteria cannot spread through sitting on the toilet seat or casual contact like touching clothes. In short, the word STI itself describes that the infection can be spread only through sexual contact and not by any other means.
Will I get urine in the blood with the clap?
STD infections that cause blood in the urine are chlamydia and gonorrhea which would have originated from within the urinary tract (the bladder through which urine passes).
The medical expression for blood in urine is hematuria. There are two forms of hematuria that doctors recognize, gross hematuria (blood in the urine that is visible with the naked eye) and microscopic hematuria (blood in the urine that is only visible under a microscope). We highly recommend anyone who sees blood in their urine consult with a doctor if the symptom continues for several days.
How can I get tested for the clap?
If you experience any symptoms mentioned above or if you suspect of having the clap STD infection, then you have to consult a medical physician. He may recommend you test for gonorrhea. Generally, the gonorrhea test is done using a urine sample or cotton swab. The cotton swab is used to take a sample of discharge and cells from the infected area either in the vagina, penis, anus, throat, or urethra. Men are usually asked for urine samples. The collected sample is then sent to the lab for analysis.
Self-collection of samples at home is also possible with Gonorrhea test kits offered by some labs across all the cities in the United States.
There are many healthcare providers who offer STD testing and we have partnered with three laboratories network that offer affordable and discreet gonorrhea testing across the country. Check out the lowest gonorrhea test cost. and home-test kit price.
Is there a home test kit available for the clap?
One of our testing providers offers the Gonorrhea home-test kit. People who are not convenient in testing for STDs at an STD clinic or who do not have time to visit the lab mostly prefer the home test kits. At home, gonorrhea testing requires a sample taken using a cotton swab in the infected genital areas. Before taking the sample, read the instructions carefully mentioned in the kit and when the sample is ready, post it back to the given address.
Get your gonorrhea home-testing kit Order Now
Test provider locations
The clap, the gonorrhea STD test can be done in any US state either by going to a nearby lab or ordering a home sample kit. The details of our selected partners can be accessed above and an online booking can be made.
What is the prevalence of clap in the U.S.?
In modern times dating apps and getting into sexual contact with others without any prior knowledge of the partner is likely to be one of major the reasons behind the vast spread of the disease. And, often it is confused with other conditions like UTIs (urinary tract infections) and can go unnoticed in the first weeks of infection, gonorrhea gets easily transmitted unintentionally between partners.
Most of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases including the clap STD do not show any symptoms in the initial stage or no symptoms at all until the infection gets worse and affects the reproductive organs. So, it is vital for everyone who is sexually active to get tested for Gonorrhea, and other common STD infections at least once a year.
Also, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that patients infected with Gonorrhea STD should be treated for Chlamydia as well.